The use of ICT in education. Information and communication technologies in work. Negative impact of ICT tools on the learner
The concept of information and communication technologies (ICT) in pedagogy.
The Federal State Educational Standard contains recommendations for the use information and communication technologies(ICT) in teaching in a school setting. The transition to the new generation of the Federal State Educational Standards requires updating the professional and pedagogical training of teachers and raising their level of work with innovative technologies.
The activation of measures for the introduction of information and communication technologies appeared along with the adoption of the "Strategy for the Development of the Information Society". This document expands the horizons of information availability for all categories of citizens and the organization of access to this information. After that, the Concept of the country's socio-economic development until 2020 was adopted, according to which all state and municipal institutions should have their own websites, including educational institutions.
However, not all schools and preschool educational institutions approached the implementation of sites responsibly. So many institutions have chosen to create an inconvenient and useless resource, so to speak, for show.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight the interpretation of the term "information and communication technologies". The currently accepted definition is:
Information and Communication Technologies represent the mastery of the technology of work in an integrated multimedia environment that implements the further development of the idea of associative information received, processed and presented in various forms, taking into account the psychological and pedagogical foundations for using ICT tools in the educational process.
Undoubtedly, information technologies have long been used in Russian and foreign education. However, it should be noted that a multi-level system for presenting information on various media is currently being formed, in which traditional and new information technologies closely interact, which serve as a good help to the teacher in his hard work.
Information and communication technologies are a necessary element of modern education. Its necessity is due to the following factors:
- ICT is needed for the formation of the information society;
- The use of ICT influences qualitative changes in the structure of educational systems and in the content of education.
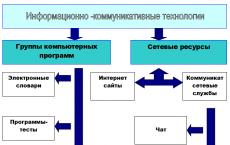
Structure of ICT
For a number of domestic teachers, the structure of information and communication technologies in education remains unclear. Currently, many modern educational programs are based on ICT competencies teachers.
ICT competence is the use of various information tools and their effective application in teaching activities.
Teachers should be able to use the main structural elements of information and communication technologies in their work. The structure of ICT is shown in Figure 2.
Having studied the structure of ICT, we can distinguish the following:
- The Internet is one of the key elements;
- The use of interactive sources of information is very important within ICT;
- The organization of classes using such elements of ICT as teleconferencing will not only broaden the horizons and improve the UUD of students, but will also improve the ICT competence of the teacher.

Figure 1. The structure of information and communication technologies
At present, practical experience has shown that information and communication technologies or ICT have a number of important didactic opportunities, which include:
- the possibility of prompt transmission over any distance of information of any volume, any form of presentation;
- storage of information in the memory of a PC or laptop for the required period of time, the possibility of editing, processing, printing, etc.;
- the ability to access various sources of information via the Internet, work with this information;
- the possibility of organizing electronic conferences, including in real time, computer audio conferences and video conferences;
- the ability to transfer the extracted materials to your media, print and work with them as and when it is necessary for the user.
Functions of ICT
Information and communication technologies have a number of functions that determine the role of ICT in the development of modern education. The most important ICT functions are didactic. The didactic functions of ICT are shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Didactic functions of ICT
As we can see, ICT has very useful didactic functions, each of which can improve the educational process. At the same time, one should not forget that one of the functions of ICT is an incentive for the self-development of the teacher and the ability to improve the level of UUD students.
Separately, it should be highlighted the fact that ICT is important for the implementation of such general educational universal actions as:
- search for information in the individual information archives of the student, the information environment of the educational institution, in federal repositories of educational information resources;
- fixing information about the world around and the educational process, including using audio and video recording, digital measurement, digitization for the purpose of further use of the recorded;
- knowledge structuring, organization and presentation in the form of conceptual diagrams, maps, timelines and family trees;
- creation of hypermedia messages;
- preparing a speech with audio-visual support;
- building models of objects and processes from structural elements of real and virtual constructors.
Means of information and communication technologies (ICT)
Information and communication technologies cannot realize their functions without funds. Key means of information and communication technologies are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. ICT tools
|
ICT tool |
Description of the ICT tool |
|
|
Computer, laptop |
Universal information processing device. A PC or laptop allows you to freely process any information. In addition, with the help of the Internet, a computer helps to find and process the information the user needs. |
|
|
Allows you to record on paper information found and created by students or a teacher for students. For many school applications, a color printer is necessary or desirable. |
||
|
A device for transferring pictures, photos to a computer for further processing. |
||
|
Projector |
It is necessary for pedagogical activity, as it increases: the level of visibility in the work of the teacher, enables students to present the results of their work to the whole class, audience. |
|
|
interactive board |
An interactive whiteboard is a touch screen connected to a computer, from which an image is transmitted to the whiteboard by a projector. Just touch the surface of the board to start working on the computer. Special software for interactive whiteboards allows you to work with texts and objects, audio and video materials, Internet resources, make handwritten notes directly on top of open documents and save information. |
|
|
Devices for recording visual and audio information (camera, video camera, phone, tablet) |
These devices belong to ICT on the basis that they make it possible to directly include information images of the world around in the educational process. |
|
|
Storage media (flash drive, SSD) |
Used to store and quickly transfer information from one computer to another. |
Having considered the key ICT tools, it is important to note that the very fact of using information and communication technologies makes it possible to optimize the learning process. This is due to the fact that technical support for lessons creates more comfortable psychological conditions, removes psychological barriers, strengthens the role of students in choosing the means, forms and pace of studying various topics of the school curriculum, improves the quality of education by providing an individual approach to learning.
ICT tools are very important for the full-fledged organization of a modern lesson. It is important to emphasize that multimedia teaching aids help to clearly build the structure of the lesson, to design it aesthetically.
Lesson outline plan using ICT
The outline of a modern lesson is unthinkable without the use of information and communication technologies, or, in other words, ICT. Currently, teachers use not only plan notes, but more and more often technological maps of the lesson.
The lesson plan contains a list of only those information and communication technologies that the teacher used. Below is an example of a plan-outline of a mathematics lesson in the first grade, during which information and communication technologies were used.
Topic: Polyline and its link (Grade 1)
Lesson type: a lesson of general methodological orientation.
The purpose of the lesson: Give an idea of the concepts: polyline, polyline link, vertices, closed polyline, open polyline.
Tasks:
- introduce students to the broken line, its parts and types.
- teach to highlight a broken line among other shapes.
- to form the skills of correct line construction.
- develop speech, attention, memory, thinking of students;
- develop temporal and spatial representations.
- contribute to the education of a healthy lifestyle, punctuality of love for the subject.
Planned results:
- know and understand what a broken line is;
- successfully determine the link of the polyline, vertices;
- know what a closed and open polyline is.
- compare your conclusions with the text of the textbook;
- check the correctness of the task;
- work in pairs.
Equipment: Computer with multimedia projector, presentation, textbook: M.I. Moro, S.I. Volkova, S.V. Stepanova "Mathematics" Grade 1 Part 1, typesetting sheets, counting sticks, ruler, pencil.
Lesson structure:
- Organizational.
- Knowledge update.
- Work on the topic of the lesson.
- Fizkultminutka.
- Independent work.
- Consolidation of the studied material.
- Reflection.
- Homework.
During the classes:
|
Lesson stage |
Teacher activity |
Student activities |
|
|
Organizational stage |
Before the lesson, the class is divided into 3 groups. Since there are 29 people in the class, 2 to 9 and one group of 10 people are formed. Teacher: Hello guys. Glad to see you at the math lesson on the topic "A broken line. A link of a broken line." Why didn't you take your seats? |
Each group chose a captain in advance. The teams were named: red, yellow and white. With a ring, the groups line up at the door behind the captain, in a chain. From the threshold of the class towards the desktop of each group, 3 satin ribbons are laid on the floor: red, yellow, white. Ribbons do not bend, they lie straight, but their length is not enough to reach your table. Groups are invited to go through and take their workplace stepping only on ribbons of "their" color. They go in single file. Then they stop abruptly. The students greet each other but continue to stand. |
|
|
Knowledge update |
Why didn't you take your seats? Teacher: Why wasn't there enough tape? Teacher: Can I also straighten each ribbon forward and you follow it further to your table? Teacher: What to do? How can we start the lesson? Teacher: Let's do it. The teacher gives the captains of each team a new ribbon. Teacher: Well, here we are. Let's look at slide 2. I replaced your ribbons with lines of the same color. Teacher: Look, that's how you walked at first. What can you say about these lines? Teacher: How can they continue? Open notebooks. Draw your line as you see it on the screen, of any length. Continue it. The teacher glances at the work. Teacher: Look at slide 3. Teacher: What's the name Teacher: But if we go like this, we won’t reach the place, the desks interfere. I saw in the notebooks of several students the following lines: Slide 4. Teacher: Tell me, is it possible to choose such a path by movement? Teacher: -Will it be a rectilinear movement? Teacher: Is it then possible to call such a line a straight line? Teacher: Let's think about what we will do in the lesson? Teacher: You almost guessed right. Only this line is called differently. You have long dry pasta on your table. (For each member of the group). Take them in your hands and bend them as shown on the slide. Fright, exclamation, chagrin. What happened? They broke. So we will also break our straight line and call it "broken". So, the topic of our lesson: "A broken line and its features." |
Students: The tape is over, it was not enough. Students: It's short. Students: No. You will have to climb on or under the desks, jump over the desks. Students consult in groups. After consulting, the captains of each group give answers. The correct answer sounds like this: The tape can be continued, but it needs to be bent, crumpled. Students bend them and lay their own routes for groups. Students: They are straight. The ends are not limited, they can be continued. Students: Do it. The teacher glances at the work. Students: Rectilinear. Students: Yes. Students: No. Students: No. The students are conferring. After that, the captain of each team stands up and announces the proposed name of the topic of the lesson. Correct answer: We will study an indirect, curved line. Students mostly break pasta. |
|
|
Work on the topic of the lesson. |
Teacher: Let's learn to distinguish a straight line from a broken line. Look at slide 5. Teacher: Think in groups and write in notebooks: Group 1: numbers of straight lines; Group 2: numbers of broken lines; Group 3: non-line numbers. Teacher: Lines No. 2, No. 5, No. 4 remain on the slide. What do you think the remaining lines have in common? Teacher: Can we say that broken lines No. 2, No. 5 are not limited in space? Teacher: Are broken lines unlimited by points along their entire length? Teacher: Look at slide 6. Teacher: What conclusion did you come to? |
Students complete the task. Most likely, this question will cause difficulty for all students. Students: Yes, because there are no dots at their ends. Students consult in groups. No. In the middle are limited. Students: Broken lines are made up of segments. |
|
|
Physical education minute |
And now a little warm-up: Now, guys, get up. Raised hands quickly Sideways, forward, backward. Turned to the right, to the left, Quietly sat down, again for the cause. (Children show answers in motion (tilts, turns, ki, claps).) You see the butterfly is flying You see, the butterfly flies, (We wave our winged arms.) He counts flowers in the meadow. (We count with a finger) One, two, three, four, five. (Clap hands.) For a day, for two and for a month ... (We walk in place.) Six seven eight nine ten. (Clap hands.) Even the wise bee (We wave our winged arms.) |
||
|
Independent work |
Teacher: How is the girl doing? Teacher: Read the text below the picture. Teacher: What did you learn? Teacher: Look at the screen on slide 8. Think about how the first group of broken lines differs from the second group? Teacher: The broken lines of the first group are called open, the broken lines of the second group are called closed. Open the canvases. Look at the group of open polylines. Put in those numbers. How many links each broken line has. Teacher: What is the smallest number of links? Teacher: The largest number of links? Teacher: How did you arrange the numbers? Teacher: Put the numbers in decreasing order. Teacher: What is the name of this order? Teacher: Look at the group of closed broken lines. On the slide - group number 2. What shapes do you recognize? |
Students: The girl is walking along a broken line. Students: The segments of the polyline do not lie on one straight line and are called links. The ends of each link are the vertices of the polyline. Students: Some lines can continue, they can complete the links, while others cannot. Students: On typesetting canvases: Students: Three. Students: Six. Students: In ascending order, in ascending order. Students: From the largest number - 6 to the smallest - 3 Students: Descending. Students: Triangles (3 corners, 3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 corners, 4 sides), pentagons (5 corners, 5 sides. |
|
|
Consolidation of the studied material |
Teacher: Remember how to draw correctly? (p. 38 of the textbook, below) Teacher: Read the task at the bottom of the page. Do it in your notebook. Teacher: Captains, check the task in groups. Who was wrong? Why? |
Pupils: We lead the pencil, tilting it in different directions, without taking our hands off, to the top. We hold the ruler, firmly pressing it to a sheet of paper, with our left hand. (Completing a task) Students analyze the errors in each team. |
|
|
Reflection |
The teacher asks questions summarizing the lesson: What new did we learn today at the lesson? What helped you learn so much about broken lines? Where will your knowledge come in handy? How did you work in class? |
Students respond and evaluate the quality of their work. |
|
|
Homework |
Teacher: Thanks for the lesson. Now write down your homework. It is not simple. You need to draw closed and open polylines of your choice and determine the number of links. |
Students write the assignment in their notebooks. |










Literature
- Besperstova Irina Vitalievna Organization of the educational process using information computer technologies // URL: http://festival.1september.ru/articles/592048/
- Information and educational environment as a condition for the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard At 3 hours Part 1 / Edited by T.F. Esenkova, V.V. Zarubina. - Ulyanovsk: UIPCPRO, 2011.
- Strategy for the Development of the Information Society in the Russian Federation dated February 7, 2008 N Pr-212 // URL:
Means of information and communication technologies are software, software, hardware and technical means and devices that operate on the basis of microprocessor, computer technology, as well as modern means and systems for broadcasting information, information exchange, providing operations for the collection, production, accumulation, storage, processing, transmission of information and the ability to access information resources of local and global computer networks.
The most commonly used ICT tools in the educational process include:
- 1) electronic textbooks and manuals demonstrated using a computer and a multimedia projector;
- 2) electronic encyclopedias and reference books;
- 3) simulators and testing programs;
- 4) educational resources of the Internet;
- 5) DVD and CD discs with pictures and illustrations;
- 6) video and audio equipment;
- 7) research work and projects;
- 8) interactive board.
Methodists distinguish several classifications of ICT tools. In accordance with the first classification, all ICT tools used in the education system can be divided into two types: hardware (computer, printer, scanner, camera, video camera, audio and video recorder) and software (electronic textbooks, simulators, test environments, information websites, Internet search engines, etc.).
The breakthrough in the field of ICT, which is currently taking place, forces us to reconsider the issues of organizing information support for cognitive activity. Thus, the second classification of ICT tools allows us to consider the possibilities of using information technologies in educational activities:
- 1) to search for literature on the Internet using browsers such as Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, etc., various search engines and online programs (Yandex.ru, Rambler.ru, Mail.ru, etc.) and work with it (abstracting, taking notes, annotating, citing, creating slide presentations online);
- 2) for working with texts using the Microsoft Office package of basic application programs: Microsoft Word allows you to create and edit texts with graphic design; Microsoft Power Point allows you to create presentation slides for a more colorful presentation of the material; Microsoft Excel allows you to perform calculations, analyze and visualize data, and work with lists in tables and web pages; Microsoft Office Publisher allows you to create and modify booklets, brochures, etc.;
- 3) for automatic translation of texts using translator programs (PROMTXT) and electronic dictionaries (AbbyLingvo7.0);
- 4) for storage and accumulation of information (CD-, DVD-disks, Flash-disks);
- 5) for communication (Internet, email, Skype, Hangout, etc.);
- 6) for processing and playing graphics and sound (Microsoft Media Player, zplayer, CorelDraw, PhotoShop image viewers), programs for creating diagrams, drawings and graphs (Visio, etc.).
The listed ICT tools create favorable opportunities in foreign language lessons for organizing independent work of students. They can use computer technologies both for studying individual topics and for self-control of the acquired knowledge. Moreover, the computer is the most patient teacher, capable of repeating any tasks as much as necessary, achieving the correct answer and, ultimately, automating the practiced skill.
Multimedia presentations are widely used by almost all teachers. They are convenient for both teachers and students. With basic computer literacy, you can create original educational materials that captivate, motivate and aim students for successful results. The educational potential of multimedia presentations can be effectively used in foreign language lessons to provide visual support for speech learning.
The advantages of multimedia presentations are as follows:
- -combination of various textual audio and video visibility;
- - the possibility of using for presentation as an interactive, multimedia board, which allows you to more clearly semantize new lexical, grammatical and even phonetic material, as well as provide support support in teaching all types of speech activity;
- - the ability to use individual slides as handouts (supports, tables, diagrams, graphs, diagrams);
- - activating the attention of the whole class;
- - ensuring the effectiveness of perception and memorization of new educational material;
- - monitoring the assimilation of new knowledge and systematization of the studied material;
- - a combination of classroom and extracurricular independent work of students; saving study time;
- - the formation of computer multimedia competence of both teachers and students, the development of their creative abilities in the organization of educational work.
The advantages of introducing Internet technologies in the process of teaching a foreign language are now beyond doubt. There is also no doubt about the positive impact of various forms of synchronous and asynchronous Internet communication (e-mail, chat, forums, web conferences) on the formation of foreign language communicative competence of students.
Network resources are an invaluable basis for creating an information-subject environment, education and self-education of people, meeting their personal and professional interests and needs. However, in itself, the availability of access to Internet resources is not a guarantee of fast and high-quality language education. Methodically illiterate work of students with Internet resources can contribute to the formation of not only false stereotypes and generalizations about the culture of the country of the language being studied, but even racism and xenophobia.
Educational Internet resources should be aimed at the integrated formation and development of:
- - Aspects of foreign language communicative competence in all the variety of its components (linguistic, sociolinguistic, sociocultural, strategic, discursive, educational and cognitive);
- - Communicative-cognitive skills to search and select, generalize, classify, analyze and synthesize the information received;
- - Communication skills to present and discuss the results of working with Internet resources;
- - Ability to use Internet resources for self-education in order to get acquainted with the cultural and historical heritage of various countries and peoples, as well as to act as a representative of their native culture, country, city;
- - Ability to use network resources to meet their informational and educational interests and needs.
Didactically, the Internet includes two main components: forms of telecommunications and information resources.
The most common forms of telecommunications (i.e. communication via Internet technologies) are e-mail, chat, forum, ICQ, video, web conferences, etc. Initially, they were created for real communication between people located at a distance from each other , and now they are used for educational purposes in teaching a foreign language.
Internet information resources contain text, audio and visual material on various topics in different languages. Educational Internet resources (IR) are created solely for educational purposes.
In the English-language literature, five types of educational Internet resources are distinguished:
- 1) hotlist;
- 2) treasure hunting;
- 3) subject sampler;
- 4) multimedia scrapbook;
- 5) webquest.
These terms are translated into Russian using transliteration. The structure and methodological content of each of these IRs is as follows:
Hotlist (list by topic) - a list of sites with text materials on the topic under study. To create it, you need to enter a keyword into a search engine.
Multimedia scrapbook (multimedia draft) is a collection of multimedia resources, unlike a hotlist, in a scrapbook, in addition to links to text sites, there are also photos, audio files and video clips, graphic information, animated virtual tours. These files can be easily downloaded by students and used as an informative or illustrative material in the study of a particular topic.
Treasure hunt (treasure hunt), in addition to links to various sites on the topic under study, also contains questions on the content of each site. With the help of these questions, the teacher directs the search and cognitive activity of students. In conclusion, students are asked one more general question for a holistic understanding of the topic (factual material). A detailed answer to it will include answers to more detailed questions on each of the sites.
The sample subject is the next level of complexity compared to the treasure hunt. It also contains links to text and multimedia materials on the Internet. After studying each aspect of the topic, students need to answer the questions posed, but the questions are not aimed at the actual study of the material, but at the discussion of discussion topics. Students need not only to familiarize themselves with the material, but also to express and argue their opinion on the discussion issue being studied.
Webquest (Internet project) is the most complex type of educational Internet resources. This is a scenario for organizing student project activities on any topic using Internet resources. It includes all components of the four materials listed above and involves a project involving all students. One of the scenarios for organizing PD can be as follows. From the beginning, the whole class gets acquainted with general information on the topic, then the students are divided into groups, each group gets a certain aspect of the topic. The teacher needs to select the necessary resources for each group in accordance with the aspect being studied. After studying, discussing and fully understanding the specific problem in each primary group, students regroup so that each new group has one representative of the primary group. In the process of discussion, all students learn from each other all aspects of the problem under discussion.
Each of the five types of educational Internet resources follows from the previous one, gradually becoming more complex and thus allowing solving more complex educational problems. The first two are aimed at searching, selecting and classifying information. The rest contain elements of problem-based learning and are aimed at enhancing the search and cognitive activity of students.
The possibilities of educational Internet resources are most fully manifested in specialized training and elective courses, when it is foreign language communicative competence, and not knowledge of the language, that plays a leading role in the educational process.
The latest information and communication technologies occupy an increasing place in the life of a modern person. Their use in foreign language lessons increases the motivation and cognitive activity of students, broadens their horizons and allows you to apply a student-oriented technology of interactive teaching a foreign language, i.e. learning in interaction.
The use of information and communication technologies in the educational process helps to intensify and individualize learning, increases interest in the subject, and makes it possible to avoid subjective assessment.
The use of a computer and digital educational resources in teaching English helps students overcome the psychological barrier to using a foreign language as a means of communication.
Information and communication technologies are both a means of presenting material and a controlling tool. They provide high quality presentation of the material and use various communication channels (text, sound, graphic, touch, etc.). New technologies make it possible to individualize the learning process in terms of the pace and depth of the course. Such a differentiated approach gives a great positive result, because creates conditions for the successful activity of each student, causing positive emotions in students, and thus affects their learning motivation.
Unlike traditional methods, when using interactive forms of education, the student himself becomes the main acting figure and himself opens the way to the assimilation of knowledge. The teacher acts in this situation as an active assistant, and his main function is to organize and stimulate the learning process.
The following digital educational resources are used in foreign language lessons: presentations in Power Point (PP), text editors, spreadsheets, tests, training programs on CD-ROM, electronic textbooks, educational Internet resources.
Multimedia presentations, e-learning programs and educational Internet resources have a great educational potential.
Thanks to the use of new information technologies in the process of teaching a foreign language, new opportunities open up for creating conditions close to the conditions of real communication in the country of the language being studied: authentic, relevant, multimedia or textual information to be learned in a foreign language can be obtained at any time and in anywhere. At the same time, it is quite easy to organize written or oral communication with native speakers or other learners of this language. Thus, there is an integration of electronic media into the traditional lesson in a foreign language: teaching aids are increasingly supplemented with relevant, authentic texts or relevant audio, video, and graphic material.
the Russian FederationMinistry of Education
Municipal educational institution
Paltsovskaya secondary school
"The effectiveness of the use of ICT in education"
Teacher:
Polyakova Yulia Alexandrovna
Bryansk 2011
1 Justification of the methodological problem_______________________________5
2 Goals and objectives of the use of ICT__________________________________6
Learning process _____________________9
4 Types of ICT implementation ___________________________________________10
5 Forms of use of ICT ____________________________________________11
6 Electronic textbooks _________________________________________________ 13
7 Control of knowledge in the lesson ______________________________________________14
The study of mathematics is currently associated with a number of features, if not difficulties in the development of school education in our country. The role of mathematics as an academic subject is extremely important in terms of shaping the worldview and creative thinking of students, not only in the field of natural science, but also in the most general sense. Knowledge, the solid foundations of which are formed during the study of mathematics at school, should be as close as possible to real life and everyday practice. The study of mathematics should be carried out in such a way that students see science in constant historical development and, wanting to study it, experience satisfaction and joy from the process of cognition.
The changes taking place today in modern society largely determine the features and the need to make changes in the activities of the teacher. In modern conditions, in educational activities, it is important to focus on the development of cognitive independence of students, the formation of research skills, and the individualization of the goals of education. It is impossible to solve this problem by the old methods. This prompted me to work aimed at improving the quality of students' knowledge, developing their creative abilities through new information technologies.
1 Justification of the methodological problem
Today, the question remains open: "How to most effectively use the potential of modern information and communication technologies in teaching schoolchildren, including teaching mathematics?" Therefore, the methodological problem that I have been working on lately is “The use of information and communication technologies in mathematics lessons as a means of increasing learning motivation”.
The task of the school is not only to communicate a certain amount of knowledge to students, but also to develop their cognitive interests, creative attitude to work, the desire to independently “acquire” and enrich knowledge and skills, and apply them in their practical activities. The main work of our children is teaching, and therefore it is very important to teach them to study intelligently. It is generally recognized that mathematics is the most time-consuming subject, requiring students to constant, painstaking and significant independent work, moreover, very specific and diverse. So one of the main tasks of a mathematics teacher is the formation and development of skills in the study of mathematics, elements of the culture of learning and thinking. To do this, it is necessary to work out in detail the content aspect of education and select from the whole variety of methods, forms, technologies those that will lead students to assimilate the conceptual components of the training program, allow them to develop the cognitive abilities of students, their activity in educational activities, and also ensure the formation and development of communicative competencies. students. The increase in mental load in mathematics lessons makes us think about how to maintain students' interest in the subject being studied, their activity throughout the lesson. In order to maintain interest in the subject and make the educational process of high quality, I actively use information technology in the lessons. Active work with a computer forms in students a higher level of self-educational skills and abilities - analysis and structuring of the information received. At the same time, it should be noted that new teaching aids make it possible to organically combine information-communicative, personality-oriented technologies with methods of creative and search activity. Today, the introduction of computer technology in the educational process is an integral part of school education. It is generally recognized that the use of computer technologies in education is inevitable, since the effectiveness of training and the quality of emerging knowledge and skills are significantly increased.
2 Goals and objectives of the use of ICT
The goals of using a computer and other information technologies in mathematics lessons are as follows: development of interdisciplinary connections between mathematics and computer science; formation of computer literacy; development of independent work of students in the classroom; implementation of an individual, personality-oriented approach.
My tasks as a mathematics teacher are as follows:
Provide fundamental mathematical training for children;
· Form informational and methodical culture, creative style of students' activity;
· Prepare students to use information technology and other information structures.
The use of ICT in mathematics lessons allows the teacher to reduce the time to study the material due to the visibility and speed of work, to check students' knowledge in an interactive mode, which increases the effectiveness of learning, helps to realize the full potential of the individual - cognitive, moral, creative, communicative and aesthetic , contributes to the development of intelligence, information culture of students.
The use of ICT in the educational process involves improving the quality of education, i.e. solving one of the pressing problems for modern society.
The process of organizing schoolchildren's education using ICT allows:
· do this process interesting, on the one hand, due to the novelty and unusualness of this form of work for students, and on the other hand, to make it fascinating and bright, varied in form through the use of multimedia capabilities of modern computers;
effective solve the learning problem, expand the possibilities of visualizing educational material, making it more understandable and accessible for students to freely search for the educational material necessary for schoolchildren in remote databases through the use of telecommunications, which will further contribute to the formation of students' need for search actions;
· individualize the learning process due to the presence of multi-level tasks, due to immersion and assimilation of educational material at an individual pace, independently, using convenient ways of perceiving information, which causes positive emotions in students and forms positive learning motives;
· liberate students when answering questions, because the computer allows you to record the results (including without grading), correctly responds to errors; independently analyze and correct the mistakes made, adjust their activities due to the presence of feedback, as a result of which self-control skills are improved;
· carry out independent educational and research activities(modeling, project method, development of presentations, publications, etc.), thereby developing creative activity among schoolchildren.
The modern information society sets the task of preparing graduates capable of:
Flexibility to adapt to changing life situations
Think independently critically
· competently work with information;
· to be sociable, contact in various social groups; independently work on the development of their own morality, intellect, cultural level.
The use of information technology in education is based on human physiology data: 1/4 of the material heard, 1/3 of what is seen, 1/2 of what is seen and heard, 3/4 of the material remains in the human memory if the student is actively involved in the process.
In order to intensify learning, along with the classical forms of teaching previously used in teaching mathematics at school and in the independent work of students, software for educational disciplines is increasingly being used: textbook programs, simulator programs, dictionaries, reference books, encyclopedias, video tutorials, libraries of electronic visual aids , themed computer games .
The capabilities of a computer, when using additional technologies adapted to it: software products, the Internet, network and demonstration equipment, constitute the material base of information and communication technologies.
3 Use of ICT in the stages
learning process
Information technology, in my opinion, can be used at various stages of a mathematics lesson:
Self-learning with the absence or denial of the teacher's activities;
Self-study with the help of a teacher-adviser;
Partial replacement (fragmentary, selective use of additional material);
Use of training (training) programs;
Use of diagnostic and control materials;
Performing home independent and creative tasks;
Using a computer for calculations, plotting graphs;
The use of programs that simulate experiments and laboratory work;
Use of gaming and entertaining programs;
Use of information and reference programs.
Insofar as visual-figurative components of thinking play an extremely important role in human life, then using them in the study of material using ICT improve learning efficiency:
Graphics and animation help students understand complex logical mathematical constructions;
The opportunities provided to students to manipulate (explore) various objects on the display screen, change the speed of their movement, size, color, etc. allow children to assimilate educational material with the fullest use of the sense organ and communication connections of the brain.
The computer can be used at all stages of the learning process: when explaining new material, consolidating, repeating, controlling, while for the student it performs various functions: a teacher, a working tool, an object of study, a collaborating team.
The computer allows you to enhance the motivation of learning through an active dialogue between the student and the computer, the variety and brilliance of information (text + sound + video + color), by orienting the teaching to success (allows you to complete the solution of any problem, relying on the necessary help), using the game background of communication between a person and machine and, importantly, endurance, calmness and "friendliness" of the machine in relation to the student.
When choosing the conditions for the use of ICT, I take into account:
Availability of programs relevant to the topic being studied;
Number of computerized workplaces;
Willingness of students to work using a computer;
The ability of the student to use computer technology outside the classroom.
4 Types of ICT implementation
Keeping in mind the words of K. F. Gauss that “mathematics is a science for the eyes, not for the ears”, I believe that mathematics is one of those subjects in which the use of ICT can activate all types of educational activities: learning new material, preparation and verification of homework, independent work, verification and control work, extracurricular work, creative work. Based on the use of ICT, many methodological goals can be implemented more effectively.
Information technology, according to G.K. Selevko can be implemented in three versions:
· as "penetrating" (use of a computer in the study of individual topics, sections, to solve individual didactic tasks);
as the main one (the most significant in the pedagogical technology used);
· as a monotechnology (when all training and management of the educational process, including all types of diagnostics, control and monitoring, are based on the use of a computer).
Of course, the ideal option that every teacher strives for is monotechnological education, i.e. independent educational work of the child in an interactive learning environment using ready-made e-learning courses. The use of information technology must be considered in the inseparable unity of all components of the educational process:
creation of lessons using IT;
creative project work of students;
distance learning, competitions;
library, Internet resources;
· elective courses;
· socio-psychological monitoring of the formation of the student's personality;
creative interaction with teachers.
5 Forms of use of ICT
In the process of teaching mathematics, information technology can be used in various forms. The directions I use can be represented in the form of the following main blocks:
· multimedia scenarios of lessons;
checking knowledge in the classroom;
preparation for the exam (special course)
extracurricular activities
Multimedia lesson plans. One of the benefits of using ICT is the dramatic increase in independent work time. Such a learning process allows you to develop thinking, activate thought processes. The work will be creative if it manifests the students' own idea, sets new tasks and solves them independently with the help of newly acquired knowledge.
The use of multimedia in lessons implements the following principles:
The principle of visibility. Allows you to use illustrative material, audio material, resources of rare illustrations in any lesson. The visibility of the material increases its assimilation by students, because. all channels of perception of students are involved - visual, mechanical, auditory and emotional.
The principle of natural conformity . The use of Internet materials is of interest to high school students. The use of multimedia presentations is advisable at any stage of studying the topic and at any stage of the lesson. The presentation of educational material in the form of a multimedia presentation reduces the time of learning, frees up the resources of children's health.
The principle of strength. The use of presentation lessons technically allows you to repeatedly return to the studied or studied material. The use of tutorials allows you to recall the material of previous lessons in one lesson.
Scientific principle: the transformation of this principle in multimedia learning gets a more fundamental basis.
Accessibility principle: this technology is integrated with the technology of differentiated learning and allows you to simultaneously display multi-level tasks, control and test tasks, tasks of increased complexity on the monitor or screen at the same time.
System principle: the use of presentation lessons allows you to develop a system of lessons on one topic, as well as displaying elements of previous lessons on the screen, to explain the new.
Sequence principle: as in traditional lessons, the educational material is remembered in a larger volume and more firmly.
I practice conducting such lessons both when presenting new material and when repeating the past.
6 Electronic textbooks
Among the main advantages of the formation of material on electronic media, in my opinion, one can note the heterogeneity of educational material (text, illustrations, animation), interactivity, instant search. All this information wealth, which opens up great prospects for the teacher, is, of course, impossible on paper. An electronic textbook has a number of undoubtedly positive properties that distinguish it favorably from traditional textbooks - the text of the textbook is accompanied by a large number of slides and video clips that enhance students' emotional and personal perception of the material being studied; the use of such a textbook allows you to do much more in the lesson than with the help of traditional means, to increase interest in the subject of mathematics. In my lessons I use disks of educational and methodological support in mathematics. However, not all disks available in the school media library, training programs do not always correspond to the material being studied, do not take into account the characteristics of the class, the content of the program. Therefore, I do not use them in full, but specific topics or tasks.
According to the functional purpose, computer programs can be conditionally divided into four main types:
informational and illustrative (replace conventional visual aids and traditional audio-visual teaching aids);
developing programs (focused on the development of memory, attention, logic, spatial thinking of students);
training programs (involving research work of students at the computer or simulator programs to obtain certain skills);
control programs (most often programs for testing the level of student learning. Such programs involve an individual survey of each student).
Among the sources of information, the Internet should be especially noted, I recommend to students sites where theoretical material is collected, as well as sites where students can independently check the level of their preparation, tests on-line.
The Internet is primarily an important source of information. In connection with the growth of information volumes, it is necessary to form an information culture. It is understood as knowledge of sources of information, techniques and methods of rational work with them, their application in practical activities. Therefore, together with a mathematics teacher, students use the resources of the Internet
7 Knowledge control in the lesson
In this block, the principle of accessibility is implemented, the computer acts as a working tool as a means of preparing and storing tasks and tests and assessing students' knowledge.
8 Testing using a computer
The teacher enters the test into the computers in advance and asks the students to complete it. The student works independently for 5-10 minutes. The volume and nature of the tasks allow you to reveal knowledge in 5-10 minutes. A student is able to complete such work on a blackboard or in a notebook within 15-20 minutes.
There are several possible answers for one task. If the student answers incorrectly, a hint appears: the corresponding rule and examples. If the error is repeated, the correct answer appears. The sequence of erroneous actions of the student is accompanied by the display of comments on the screen. The work ends with the display of statistical information about the number of errors and the score. As a result, the teacher sees real knowledge, and the students have no complaints against the teacher for the mark.
One of the most effective methods of preparing for the exam is the method of solving test tasks. The practical application of test technologies in preparing for the Unified State Examination showed that students who are familiar with the methods of working on tests are superior in terms of their level of preparation to schoolchildren who prepared using ordinary textbooks and problem books, which, of course, cannot be ruled out. Students who are interested in passing the exam already in the 10th grade acquire disks with tests, complete test tasks, and train themselves.
To control knowledge in the classroom, in addition to traditional control and measuring materials, I use specially compiled multimedia presentations and tests.
I believe that it is important to teach students to work with the test and in interactive mode with a computer, for this I use the program for creating tests "Simylator", as well as disks - preparation for the exam from the "Tutors of Cyril and Methodius" series.
Conclusion
A school lesson is a social order of society in the education system, which is determined by the socio-psychological needs of society, the level of its development, the moral and moral values of this society. Unfortunately, the process of modernization in the education system is difficult. This is due to the fact that teachers aim students only at obtaining solid theoretical knowledge, some of which, in my opinion, will not receive practical application in the future life.
It is no secret that the current practice of teaching mathematics is characterized by the traditional study of mathematical formulas, the abstractness of mathematical concepts, which are usually memorized mechanically.
In my opinion, in mathematics lessons, the stated problem can be solved to some extent by using computer technologies, which, firstly, are based on a strict algorithm of student actions. After all, not every student, having learned the rules, can use them. The use of algorithms, maps, tables, that is, orienting schemes, streamlines the learning process .
Secondly, in connection with the acute problem of saving time in the course of the educational process, the modern school is also faced with the task of finding the means and methods of teaching that make it possible to save time as much as possible in the lesson. In my opinion, the use of a computer in the classroom is one such means.
Thirdly, I believe that learning with the use of information and communication technologies is also a level differentiation, because in the conditions of this technology the student has the right to choose the content of his education, the level of assimilation. At the same time, the teacher's activity should provide an opportunity for each student to acquire knowledge at a mandatory or higher level (at the student's choice).
In accordance with the goals set, ICT should help the student to obtain better knowledge, which is necessary for the successful passing of the Unified State Exam.
Bibliography:
1.
Selevko G.K. Modern pedagogical technologies: Textbook. M.: National education, 1998. 256 p.
2. "Preparing students for the successful passing of the exam in mathematics" From the experience of the teacher of mathematics MOU secondary school No. 20 Knyshenko L.N., Stary Oskol
files -> Guidelines for organizing research and project activities for younger students
- Identification of the possibility of effective use of ICT in pedagogical activity.
- Creation of real information conditions for the development of creative activity of students and teachers.
The plan of the teachers' council:
- The relevance and significance of the use of ICT-technologies in the work of teachers.
- Types of educational technologies.
- ICT tools.
- Practical application of ICT-technologies in work.
- Findings.
- Draft decision of the teachers' council based on the study of literature, the results of interviews, speeches.
Responsible: creative group preparing the teachers' council.
Expected result: Positive activity of the teaching staff on the possibility of using modern technologies in their work.
Standard conditions: methodical office
Preparation for the pedagogical council
The course of the pedagogical council
| Stage | Content | Responsible |
| 1 | Announcement of the topic, agenda of the pedagogical council. | Director |
| 2 | Election of the secretary of the pedagogical council. | Pedagogical team |
| 3 | 1. The relevance and significance of the use of ICT - technologies in the work of teachers. 2. Types of educational technologies. 3. ICT tools. 4. Practical application of ICT-technologies in work. 5. Conclusions. 6. Draft decision of the teachers' council based on the study of literature, the results of interviews, speeches. |
Deputy Director. teachers |
| 4 | Summing up the results of the work of the teachers' council. | Pedagogical team |
Pedagogical Council
"Application of ICT-technologies in work"
1. Introduction
“... With the development of progressive ideas in education, with the promotion of ideas and principles of student-centered learning, teachers' attempts to find the tools that would ensure the stability of achieving the necessary educational outcomes by the majority of students become more active. When it comes to universal learning mechanisms, we inevitably turn to the concept of "pedagogical technologies".
The effective use of information and communication technologies (ICT) in the educational process is an urgent problem. Today, a teacher in any discipline should be able to prepare and conduct a lesson using ICT. A lesson using ICT is visual, colorful, informative, interactive, saves the time of the teacher and the teacher, allows the teacher to work at his own pace, allows the teacher to work with students in a differentiated and individual way, and makes it possible to quickly monitor and evaluate learning outcomes.
Pedagogical technology - a set of psychological and pedagogical attitudes that determine a special set of forms, methods, methods, teaching methods, educational means; it is an organizational and methodological toolkit of the pedagogical process (B.T. Likhachev);
- this is a description of the process of achieving the planned learning outcomes (I.P. Volkov);
- a set of knowledge, skills and abilities necessary for a teacher in order to effectively apply in practice the methods of pedagogical influence chosen by him both on individual pupils and on the children's team as a whole.
Educational technology is a system that includes some representation of the planned learning outcomes, diagnostic tools for the current state of students, a set of learning models and criteria for choosing the optimal learning model for given specific conditions (V.V. Guzeev).
Educational technology includes training, development and education of students.
It follows from the definitions that technology is associated to the maximum extent with the educational process - the activities of the teacher and the student, its structure, means, methods and forms.
ICT - electronic presentation of information, its processing and storage, but not necessarily its transmission.
Today, computer technology can be considered a new way of transferring knowledge that corresponds to a qualitatively new content of learning and child development. This method allows the child to study with interest, find sources of information, foster independence and responsibility in obtaining new knowledge, develop the discipline of intellectual activity.
ICT tools:
A computer is a universal information processing device.
Printer - allows you to record on paper information found and created by students or a teacher for students. For many school applications, a color printer is necessary or desirable.
Projector - radically increases: the level of visibility in the work of the teacher, the ability of students to present the results of their work to the whole class.
Screen for projecting an image from a computer.
An interactive whiteboard is a touch screen connected to a computer, from which a projector transmits an image to the board. Just touch the surface of the board to start working on the computer. Special software for interactive whiteboards allows you to work with texts and objects, audio and video materials, Internet resources, make handwritten notes directly on top of open documents and save information.
Devices for recording (inputting) visual and audio information (scanner, camera, camcorder) - make it possible to directly include information images of the world around in the educational process.
The use of information and communication technologies is a necessary condition for the modern educational process, when the main thing is not the transmission of fundamental knowledge, but the development of creative abilities, the creation of opportunities for realizing the potential of the individual. ICT is used not as a goal, but as another pedagogical tool that contributes to the achievement of the goal of the lesson.
Practical application of ICT in the classroom.
The main goal is to help children learn about the surrounding reality, develop their powers of observation, teach them to see the world around them in a wider and more versatile way, instill in them a sense of beauty, and develop personal abilities.
The main objectives of the classes of ecological and biological orientation is to familiarize students with the breadth and diversity of the field of activity. The study of different materials and means depicting nature.
How to make each lesson joyful, interesting, and most importantly - aimed at the development of each child?
Today, one cannot be a pedagogically competent specialist without studying the entire vast arsenal of educational technologies. And it is necessary to navigate a wide range of modern innovations. From the abundance of concepts, theories, technologies and methods that could help create a system of work that would take into account the characteristics of classes, in accordance with the characteristics of children and the realities of modern society.
A powerful flow of new information, advertising, the use of computer technology on television and cinema, the distribution of game consoles, electronic toys have a great influence on the upbringing of the student and his perception of the world around him. The nature of his favorite activity - games - also changes significantly, and his favorite heroes and hobbies also change. A modern student does not sit in the classroom, which are held according to the "classical scheme", calmly absorbing, like a sponge, all the knowledge prepared for him. A modern student assimilates only the information that interested him most, the closest to him, which evokes pleasant and comfortable feelings, that which bothers him the least. Therefore, one of the means that has a unique opportunity to increase the motivation and individualization of the education of a modern student, the development of his creative abilities and the creation of a positive emotional background is a computer.
The use of a computer in the classroom becomes most natural due to such genuine children's interest. The computer successfully enters into a synthesis with school subjects, harmoniously complements it, significantly expands its capabilities and creativity.
One of the obvious advantages of a multimedia lesson is increased visibility. Let us recall the well-known phrase of K.D. Ushinsky: “Children's nature clearly requires visibility. Teach a child some five words unknown to him, and he will long and vainly suffer over them; but associate twenty such words with pictures and the child will learn them on the fly. You are explaining a very simple thought to a child and he does not understand you; you explain a complex picture to the same child, and he understands you quickly ... If you enter a class from which it is difficult to get a word (and we cannot look for such classes), start showing pictures, and the class will speak, and most importantly, will speak free…".
The use of visualization is all the more relevant because schools, as a rule, do not have the necessary set of tables, diagrams, reproductions, illustrations, or they are of poor quality. In this case, the projector can be of invaluable assistance. However, the expected effect can be achieved if certain requirements for the presentation of visibility are met:
recognition of visibility, which must correspond to the presented written or oral information;
presentation dynamics. The time of the demonstration should be optimal, and correspond to the educational information being studied at the moment. It is very important not to overdo the effects;
well-thought-out image sequence algorithm.
the optimal number of presented images on the screen. You should not get carried away by the number of slides, photos, etc., which distract students, do not allow them to focus on the main thing.
Forms of using a computer in the classroom:
- use of media resources as a source of information (discs);
- computer support for the teacher's activities at different stages of the lesson;
- using a computer to perform technological maps;
- portfolio creation.
Types: presentations, slide - films and test tasks, computer tests;
- crossword puzzles, puzzles, technological cards, instructional cards
When used in the classroom, the effectiveness of learning and the quality of knowledge increase.
The use of computer technology in teaching makes it possible to differentiate educational activities in the classroom, activates the cognitive interest of students, develops their creative abilities, and stimulates mental activity.
Unfortunately, when using ICT in my classes, I encounter a number of problems:
- a small number of computers.
- different levels of preparedness and development of students;
The effective use of ICT tools in the classroom allows you to make the lesson more interesting, visual; involve students in active cognitive and research activities; strive to realize themselves, to show their capabilities.
Thus, the use of ICT tools allows:
- to activate the cognitive activity of students;
- conduct classes at a high aesthetic and emotional level;
- provide a high degree of differentiation of training (almost individualization);
- increase the amount of work performed in the classroom by 1.5-2 times;
- improve knowledge control;
- rationally organize the educational process, increase the effectiveness of the lesson;
The effective use of ICT tools allows you to make the lesson exciting and modern. Allows for an individual approach to learning, objectively and timely control and summing up. But I think that the textbook cannot be replaced. This is just an addition to the textbook.
Classes using a computer develop perseverance, attentiveness, accuracy, develop finger motor skills, which can positively affect working with a pencil and brush. Complexes, tightness, stiffness disappear.
The use of information and communication technologies is a necessary condition for the modern educational process, when the main thing is not the transmission of fundamental knowledge, but the development of creative abilities, the creation of opportunities for realizing the potential of the individual. ICT is used not as a goal, but as another pedagogical tool that contributes to the achievement of the goal of the lesson.
1. The computer really has ample opportunities to create favorable conditions for the work of the teacher and students.
2. Brings to a qualitatively new level of application of explanatory-illustrative and reproductive teaching methods.
3. The use of ICT in the classroom allows you to diversify the forms of work, the activities of students, activate attention, and increase the creative potential of the individual.
5. Using a multimedia projector allows you to work on the text more efficiently (visually, aesthetically, saves time).
7. ICT develops the independence of students, the ability to find, select and arrange material for the lesson, using the possibilities of the Internet.
8. The use of tests not only saves time, consumables, but also gives you the opportunity to evaluate your knowledge and your capabilities.
9. Students have the opportunity to improve their computer skills.
10. The active use of ICT in the classroom leads to an increase in interest in the visual arts and the quality of education.
The range of using this technology in the educational process is very large: from being used as a visualization tool to ways of presenting educational information. At the same time, the computer is a powerful tool for increasing the effectiveness of training, it allows you to increase the motivation of students.
The effectiveness of the use of ICT in the classroom is not only possible, but also necessary, it contributes to an increase in interest in learning, its effectiveness, and develops the child comprehensively. Computer programs involve children in developmental activities, form culturally significant knowledge and skills.
Thus, the use of computer technology makes it possible to change the educational process for the better, more comfortable side, covering all stages of educational activity.
Solution project.
The use of ICT contributes to the growth of the teacher's professional skills, increasing the efficiency of mastering the skills of independent search, processing and presentation of knowledge, developing the personality of students and preparing for a comfortable life in the information society.
The first stage (preparatory) "Computer literacy"
- Creation of subject teachers' ideas about the possibility and necessity of using ICT in the educational process.
- Teaching teachers the basics of computer literacy.
- Preparing students for learning in an ICT environment.
The second stage "Introduction of ICT in education"
- Publication of educational and methodological information in various forms.
- Development of methods for using ICT in the educational process.
- Conducting a pedagogical seminar-conference
- Conducting the competition "ICT in the work of the teacher."
- Carrying out intermediate monitoring of the results of the work of teachers of the problem group.
- Technical equipment of the institution.
- Creation and updating of the website.
The third stage "Final".
- Summing up the work on the topic "Introduction of ICT in education".
- Carrying out the final monitoring of the work of the teaching staff on the introduction of ICT in the learning process.
- Systematization of the material on the methodology of using ICT in the classroom and in educational work.
- Generalization and dissemination of successful experience of pedagogical activity.
Bibliography
- Afanaseva O.V.
Svetlana Durakova
Your attention is the dissemination of work experience.
« The use of information and communication technologies in educational activities»
Informatization society has significantly changed the practice of everyday life. The same changes are reflected in the kindergarten as in a mirror.
Therefore, the aim of our work the use of information and communication technologies in educational activities is, quality improvement education through active implementation in educational educational process of information technology.
At use ICT solves such problems as:
Activation of cognitive, creative activities;
Achieving the goals of training and education with the help of modern electronic educational materials;
Skill development self-education and self-control;
Increasing the comfort level of preschoolers;
Reduction of didactic difficulties in children;
Increasing the activity and initiative of children both during GCD and in free activities
Acquisition of computer skills.
How relevant is the topic? use of information and communication technologies in the field of education.
Our children now come to kindergarten, one might say, with the initial skills of mastering new technologies. Many of them know how to use gadgets better than you and I, educators.
But if the computerization of school education in our country has almost twenty years of history, then in kindergarten the computer has not yet become a well-mastered tool for teachers. However, every year modern information Technology more and more densely enter into our lives. Accordingly, we must keep up with the times, become guides for the child to this world of new technologies.
What is ICT?
The combination of ICT is associated with two types of technologies: information and communication.
Information technology - a set of methods, methods and means of providing storage, processing, transmission and information display and focused on improving efficiency and productivity. At the present stage, methods, methods and means are directly interconnected with a computer (computer technology) .
Communication technologies define methods, ways and means of human interaction with the external environment (communication, communication).
In these communications, the computer also has its place. It provides, comfortable, individual, diverse, interaction of objects of communication.
Connecting information and communication technologies, projecting them onto educational practice, it should be noted that the main task facing their implementation is the adaptation of a person to life in information society.
Information Technology, it is not only and not so much computers and their software.
ICT means using a computer, Internet, TV, video, DVD, CD, multimedia, audiovisual equipment, that is, everything that can provide ample opportunities for communication.
Where can ICT help a modern teacher in his work?
This is work with children, work with parents and work with teachers.
When creating a single database of methodological and demonstration materials, the teacher has more free time.
Today, many kindergartens are equipped with computer rooms. But still missing:
Methodology use of ICT in the educational process,
Systematization of computer developing programs,
Unified program and methodological requirements for computer classes.
To date, this is the only type activities, not regulated by special educational program. Teachers have to independently study the approach and implement it in their own activity.
However usage ICT does not provide for teaching children the basics informatics and computer engineering.
For us it is before Total:
transformation subject-developing environment
Creation of new means of versatile development of children
use of new visibility
So way, use of information technology in the educational process, not only appropriate, but it will also allow achieving one of the goals that it sets for teachers "Modernization concept education» - preparation of a versatile developed personality.
So how am I in my work I use information and communication technologies:
In his activities I have identified the following areas use of ICT, which are available to work with preschoolers:
Creation of presentations;
Working with Internet resources;
usage ready-made training programs;
For this I using a variety of equipment:
TV sets with DVD set-top boxes,
A computer
Multimedia projector
Printer
Record player
Video and photo camera

Working with parents use presentations for leisure activities, theatrical performances, children's parties and parenting assemblies.

Working with children: organization of direct educational activities, joint activities of a teacher with children, viewing multimedia.



Selection of illustrative material for classes, design of parental corners, transformation subject-developing environment of the group, informational material for registration of stands, folders-movers.



Selection of additional educational material for classes, acquaintance with the scenarios of holidays and other events.



Exchange of experience, acquaintance with periodicals, developments of other teachers.

In preparation for classes, when looking for material regularly use internet resources, which presents a variety of pedagogical technologies, work experience of educators, the most varied visual, music and video material.



preparation of group documentation (lists of children, information about parents, diagnostics of the development of children, monitoring of the implementation of the program, etc., reports. I use a digital version of writing calendar and thematic plans. Planning is carried out in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard.
The computer will allow you not to write reports and analyzes every time, but it is enough to type the scheme once and only make the necessary changes in the future.

Create Powerpoint Presentations to Increase Efficiency educational classes with children and pedagogical competence of parents in the process of parenting assemblies.
Design of booklets, business cards of the group, materials in various areas activities.

Creation of e-mail, maintenance of your rubric on the DOW website.

Let's not forget that when organizing a child's work on a computer, many factors must be taken into account. The computer develops many intellectual skills, but we must not forget about the norm.
Sanitary standards:
Continuous duration of work with a computer in developing game classes
For children 5 years old, should not exceed 10 minutes
For children 6-7 years old - 15 minutes
For children with chronic pathology, who are often ill (more than 4 times a year, after suffering illnesses for 2 weeks, the duration of classes with a computer should be shortened:
For children 5 years old up to 7 minutes,
For children 6 years old - up to 10 minutes.
To reduce the fatigue of computer classes, it is necessary to ensure a hygienically rational organization of the working places: matching the furniture to the growth of the child, a sufficient level of illumination.
The screen of the video monitor should be at eye level or slightly lower, at a distance of no closer than 50 cm.
A child wearing glasses should work at a computer with them on. Unacceptable usage one computer for the simultaneous occupation of two or more children.
Classes for children with a computer are carried out in the presence of a teacher or parent.
So way, I come to the conclusion that they contribute to a better assimilation of the material, help to study the necessary material in a playful, fabulous way. Besides information and communication technologies contribute to an increase in cognitive interest, activate the mental children's activities. Use of information technology helps the teacher to increase the motivation for learning children.
I believe, that use of modern information and communication technologies in preschool education appropriate. This allows for a small time allotted for direct educational activities, to cover the material more widely, to present it more interesting and relevant. In addition, animated and video materials are perceived by children with pleasure, the assimilation of knowledge occurs in a relaxed manner.
Thank you for your attention!