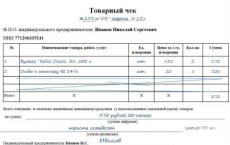
Punched cashier's check fine. Mild punishment for an unbroken check. Penalty for non-penetration of a cashier's check and other similar offenses
The fine for a check not punched at the cash desk is from ¼ to ½ of the amount of the check, but not less than 10 thousand rubles. To avoid such a situation, strict control over the sales process and the use of modern cash registers, such as SP-101 FRK, ShTRIKH-FR-K and KASBI FR-01K, are necessary.
Penalty for an unbroken check 2018 for individual entrepreneurs
In accordance with the Federal Law-290 dated 03.07.2016, non-receipt and a fine for an unbroken check in 2018 for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs have been tightened by an average of 3.5 times. According to paragraph 1. Art. 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income is recognized as revenue both produced on its own and previously acquired - goods, services and works, as well as property rights.
In paragraph 2 of Art. 14.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses clearly states that the use of CCP is mandatory when receiving income from the activities of an individual entrepreneur. The rules came into full force on July 1, 2018 for individual entrepreneurs with UTII, and for individual entrepreneurs with the simplified tax system they are valid from July 1, 2018. In Art. 2.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of Russia states that individual entrepreneurs bear the same responsibility as officials. There are no exceptions for entrepreneurs in the law. Accordingly, an unbroken check gives the tax agent every reason to apply penalties against a negligent entrepreneur.
KKT according to Art. 1.1. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003 is a technical tool used to transfer data on daily revenue in the prescribed form to the tax office. The technique allows you to quickly record data on each operation and store them in a fiscal drive; it provides recording, storage of data and their transmission through the operator to the inspection.
The cash registers used must meet the following criteria:
- there is a fiscal drive;
- there is no possibility to correct the data;
- there is a passport, sealing and personal identifier;
- official registration;
- permanent service;
- uninterrupted work.
Only with the help of the right apparatus can you knock out a check and be sure that the tax office will not make claims and will allow you to avoid a fine for not issuing a check.
Important! The penalty for non-issuance of a 2018 cash receipt is set at 25-50% of the amount in the check and at least 10 thousand rubles. According to Art. 4.5. Administrative Code of the Russian Federation, the statute of limitations for violation of the principles of working with cash registers, which will entail tax evasion, is 1 year from the date of the offense.
Example: if the check is not broken for 270 thousand rubles, then the individual entrepreneur will pay to the tax office from 67.5 to 135 thousand, and if for 5 thousand rubles. - then 10 thousand.

Repeatedly unbroken check in the event of a check in excess of the settlement amount of 1 million rubles. according to Part 3 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation entails the suspension of the activities of the IP for a period of 90 days.
Important! Only individual entrepreneurs who were convicted of an offense for the first time can avoid punishment.
After making the payment for the goods, the buyer has the right to decide what type of check he needs:
- electronic;
- on paper;
- in two versions.
The entrepreneur is obliged to provide a check: otherwise, the client has the right to file a complaint with the tax office. This will result in an unscheduled inspection of the activities of the individual entrepreneur, so you need to take into account the opinion of the buyer and not refuse to issue a receipt for payment.
Interesting fact! If the check was broken by an amount that exceeds the actual purchase amount, no penalty is provided. Moreover, the judicial practice of Russia in this case is on the side of the entrepreneur.
Who can impose a fine
Failure to break through the KKM check entails a fine that may be imposed by employees of the Federal Tax Service who make a test purchase as part of an on-site tax audit or if there are complaints from individuals against the individual entrepreneur. If the receipt was not issued to the tax officer by the cashier, he has the right to fine the individual entrepreneur, in which case an act is drawn up that will be transferred to the tax chief in order to impose a fine.

Important! The term for issuing a fine is 5-10 business days. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 70 of the Tax Code, the inspection sends a request for payment within 20 days.
After this period, the IP is sent an act to the place of registration.
When there is no penalty for not issuing a check
One of the exceptions is the fact when the buyer makes an advance payment. That is, the goods are not paid in full and remain with the seller - the purchase and sale transaction has not yet been formalized. As soon as the client pays for the purchase in full, the company is obliged to punch him the document.
How to pay a fine for not breaking a cashier's check
The mechanism for paying any fines in the tax office is the same:
- make a one-time payment to the IFTS at the place of registration, through Sberbank or the taxpayer's personal account on the website of the IFTS;
- payment is made on the basis of an act from the taxpayer on payment of a fine for failure to provide a check;
- when paying a sanction by an authorized person, a power of attorney is required;
- it is necessary to pay a fine for the absence of a fiscal receipt within 2 months;
- KBK is indicated 3000;
- payments are made in any form.
What will happen if you do not make payment to the Federal Tax Service. Postponement
If there is a delay in payment, then the tax authority will charge a penalty in the amount of 40% of the unpaid amount of the fine, since this violation is regarded as intentional and is regulated by clause 1.3 of Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is the general rule.

IP is granted a delay of 1-3 months if:
- the citizen was expelled from the territory of Russia;
- the foreigner was expelled from the territory of Russia;
- IP was arrested;
- An individual entrepreneur is in a pre-bankruptcy state or is undergoing the procedure of liquidation of a legal entity.
The deferral does not apply to:
- expelled foreigners, when the act of expulsion from the country occurred simultaneously with a fine;
- deported stateless persons under the same conditions.
After the installment period has expired, the individual entrepreneur is obliged to pay the administrative obligation. At the same time, the Federal Tax Service has the right to apply to the IP in court and then the fine will have to be paid in court.
The tax officer notifies the IP as follows:
- sends a demand for debt repayment;
- writes off money from the IP account;
- money can be withdrawn from all types of property of a person - this is subsidiary liability, i.e. An individual entrepreneur is liable for his debts with all his property.
How to avoid paying a fine for an unissued check
In case of errors in the preparation of the act by an employee of the tax inspectorate, an individual entrepreneur has the right to challenge the decision in court. Of course, you can try to negotiate peacefully: for this, the diplomatic abilities of the entrepreneur are important, but this approach does not always work. You can try to convince the tax officer by referring to the excess of authority of an official (issuing an act is in the area of competence of the head of the Federal Tax Service), and not an ordinary employee.

If the IP did not break the check, then the fine is assigned only if 2 conditions are met:
- the act must be signed by the head of the Federal Tax Service;
- the fault of the IP must be proven.
Interesting fact! Judicial practice shows that if the cashier did not break through the receipt within a few minutes, this is not a reason for issuing a sanction. Thus, if the individual entrepreneur did not break the check upon the fact of the purchase, then we can refer to the fact that he simply did not have time to do this. But it is not worth hoping that the court will definitely accept such a statement as a basis for terminating the case on an administrative offense, because according to Article 5 of Federal Law-54 of May 22, 2003, the check is knocked out at the time of the purchase, but not later.
Here are 3 more circumstances that will help to avoid liability:
- natural disasters and force majeure circumstances - deferred payment;
- documented illness;
- when the actions taken by the entrepreneur were dictated by the tax officer, but this did not lead to the payment of a fine.
Important! A difficult life situation, the fact of forcible coercion, can mitigate guilt. This will result in a 2-fold reduction in the amount of liability.
It is highly not recommended to use the above tips if they did not take place in real life. For giving false testimony, the legislation of the Russian Federation already provides for criminal liability, which definitely cannot be avoided.
Important legal information! Some individual entrepreneurs have the right to apply for the postponement of the application of CCP in their activities until July 1, 2019.
- IP on UTII (except for retail trade and public catering establishments);
- IP on PSN;
- Individual entrepreneurs in the field of retail and catering, if they do not hire employees and carry out their activities on their own.
Important! The above right does not relieve the individual entrepreneur from the obligation to issue a check at the request of the client. If the IP did not break the check, the fine is guaranteed.
A fine for selling without a receipt when selling goods and providing services is not uncommon. Selling without a receipt is a liability that is an offense and threatens the entrepreneur with a real fine. Concealment of income is punishable.
You should not tempt fate and carry goods "by the cash register": in addition to fines, you can achieve additional unscheduled inspections from the Federal Tax Service. To avoid the negative consequences of working with CCP, it is necessary to strengthen control. If the violation was committed due to inattention, try to prove the unintentionality of your actions and knock out a check.
They did not issue a cash receipt - the situation is quite common and needlessly ignored by most buyers. Failure to issue a cash receipt can complicate the process of returning the desired purchase, if suddenly the product turned out to be defective or of inadequate quality. What to do in such a situation, what sanctions threaten the seller, whether sellers should always issue a cashier's check, and when non-issuance of a check can be done legally, you will learn from this article.
Issuing a cash receipt is the responsibility of the seller or organization. After all, this small piece of paper is irrefutable evidence of the conclusion of a transaction between the consumer and the seller for the sale (acquisition) of a certain type of product. What to do in a situation where the seller did not issue a cash receipt? Claim it right on the spot! After all, the presence of this receipt will provide a guarantee that the buyer will be able to return the defective product during its warranty period. If the seller deliberately tries to persuade the buyer by force of persuasion to purchase goods without a cash receipt, then this should lead the buyer to the idea of whether it is worth doing business with such a negligent merchant.
In situations where a purchase is necessary and there is simply no other alternative, you should not despair either. The presence of witnesses to the purchase in the event of a possible exchange will benefit the buyer. In addition, the process of purchasing goods can be recorded on a video of a mobile phone, indicating the date, time and place of purchase. This is due to the provisions of the Consumer Rights Protection Law.
Seller's obligations and penalties
Sellers, on the basis of Article 5 of the Federal Law - No. 54 of May 22, 2003, when the client pays for the purchase of goods in cash, are required to issue a cash receipt. The standard rules for the operation of cash registers state that the seller, upon receipt of funds for the purchase of goods or services, must:
- State the total amount of money received from the buyer.
- Print a cash receipt indicating the name of the product or service, the date and time of its sale, the cost of the product or service. The receipt must also contain information about the name of the organization selling the goods or services, its details, other data among which the method of payment (cash or non-cash) may be indicated.
- Announce the amount of change, at the request of the purchaser.
Violation of one of these points means a violation of the sale procedure. This means that the seller can be held administratively liable in the form of a fine, the amount of which varies from 3,000 to 4,000 rubles for individuals; for legal entities, the amount of the fine is quite significant and ten times more than the amount for individuals. This is due to Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses.
There are situations where the seller may legally not issue a cashier's receipt and therefore it is imperative for potential consumers to familiarize themselves with this information. Based on Federal Law No. 54, sellers may not use a cash receipt if they offer the public to purchase a certain type of service, and instead of a cash receipt, they use strict reporting forms.
Or in cases of application of UTII and PSN, which is not a contradiction to Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But at the same time, the legal requirement, voiced by the client about the desire to receive a cash receipt, cannot be violated.
Did the sellers give you a cash receipt? Do not despair - you can file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor, the Tax Service of the Russian Federation or the Society for the Protection of Consumer Rights. These organizations have effective and efficient ways to influence negligent sellers. The most insignificant of them are test purchases, according to which the verdict of the organization is issued and, possibly, the procedure for imposing penalties is carried out. If you were not given a check, then be sure to make an entry in the book of complaints and suggestions, let other potential clients of this organization know about the dubious inclinations of a negligent seller to save on taxation and conduct business contrary to the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Remember - a cashier's check is required to be issued, only with the exception of a few of the above provisions! In difficult situations, when you were not given the coveted cash receipt, and then there were difficulties with the return of the goods, it is most reasonable to seek legal assistance from the Legal Expert company. Our specialists will be able to advise their clients in detail and tell about possible actions in this situation in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. In the most critical situations, we are ready to assist in full legal support and bringing the case to court.
In contact with
For many Russian businesses, from July 1, 2017, the law establishes an obligation to use innovative online cash registers in the course of settlements with customers. At the same time, the provisions of federal regulations define fines for non-use of a new type of cash register equipment. Let's take a closer look at these sanctions.
We will show you which cash desk from our catalog is suitable for your business.
Who is required to use online cash registers
But, before talking about the penalties provided for by law for not using online cash desks, it will be useful to study who such sanctions, in principle, can be applied to.
We are talking about trade enterprises that, from July 1, 2017, are required to use online cash registers - an innovative type of cash register equipment. Online cash desks must, in accordance with the requirements of Law No. 54-FZ, be able to:
- send data on payments made at the checkout to the Federal Tax Service via the Internet (through specialized structures - Fiscal Data Operators);
- generate cash receipts in electronic form and send them to customers (also through OFD);
- ensure the safety of payment data in the CCP memory during periods of lack of Internet connection.
Such functions of the old-style CCP - with ECLZ, do not possess. Therefore, trading businesses need to change them to online cash registers.
Subscribe to our channel in Yandex Zen - Online cash desk !
Be the first to receive hot news and life hacks!
From July 1, 2017, all trading enterprises (more precisely, everyone who sells goods to individuals) that do not fall under the exceptions established by law must use online cash registers. It should be noted that the list of such exceptions is quite wide. Moreover, you need to define it:
- considering two versions of Law No. 54-FZ at once - the current one, and the one that was put into effect on 03/08/2015;
- dividing exceptions into two categories - permanent and temporary.
Permanent exceptions are those that allow businesses that fall under them not to apply the CCP until otherwise provided by law. There are currently exceptions:
- certain provisions of paragraph 2 of Art. 2 of the Law "On the application of CCP" dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ in the current edition;
- paragraph 3 of Art. 2 of Law No. 54-FZ as amended on 03/08/2015.
At the same time, after July 1, 2018, only those exceptions that are fixed in the current version of Law No. 54-FZ will be in force (note that their list largely coincides with what is reflected in the version of Law No. 54-FZ of 08.03.2015) .
Such exceptions exempt businesses in various segments from the use of cash registers. For example, in the current version of Law No. 54-FZ, they are established for entrepreneurs who:
- sell press through newsstands;
- conduct trade in the market from tents;
- sell milk, kvass from tankers;
- repair shoes.
Temporary exceptions - those that allow businesses falling under them not to apply CCP until July 1, 2018 (and if this period is not changed by law). After - online cash desks will have to use all stores, except for those for which the law establishes permanent exceptions.
Temporary exceptions set:
- paragraph 2 of Art. 2 of Law No. 54-FZ as amended on 03/08/2015 - for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities on UTII, IP on PSN;
- clause 2.1 of Art. 2 of Law No. 54-FZ as amended on 03/08/2015 - for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities providing services to citizens.
1. Ask a question to our specialist at the end of the article.
2. Get a detailed consultation and a full description of the nuances!
3. Or find a ready-made answer in the comments of our readers.
At the same time, instead of CCP checks, such businesses are required to issue other documents to their customers certifying the fact of receiving funds from the client on account of goods or services. Namely:
- Trade checks.
They must be issued by individual entrepreneurs and legal entities on UTII or individual entrepreneurs on PSN when selling goods to individuals. The sales receipt must at the same time contain the details, the list of which is established in clause 2.1 of Art. 2 of Law No. 54-FZ. Note that a sales receipt is necessarily issued only at the request of the client.
- Forms of strict reporting.
Such an obligation is established for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities providing services to citizens. The taxation system here can be, in principle, any - UTII, PSN (for individual entrepreneurs), DOS, USN, ESHN. Strict reporting forms must contain the details established by Decree of the Government of Russia dated May 6, 2008 No. 359. At the same time, the BSO can be generated on a printed form or using special hardware and software solutions.
The form of strict reporting to the indicated firms must be issued to the client in any case - even if he did not ask for it.
It should be noted that the law may also establish “reverse” exceptions in terms of establishing the obligation to use online cash registers - when a business, exempted by one rule of law from the use of cash registers, is obliged to use online cash desks of another, later (and therefore, having higher legal force) norm of the law.
For example, on March 31, 2017, amendments to Law No. 261-FZ on state regulation of the circulation of alcoholic products came into force, according to which businesses on any taxation systems (including UTII and PSN) became obliged to use online cash desks from July 1, 2017. However, the version of Law No. 261-FZ of July 31, 2017 contains a provision that alcohol sellers conduct settlements in the jurisdiction of Law No. 54-FZ. This means that in the case of using UTII, PSN or in the process of providing services (for example, restaurants), they ceased to be obliged to use online cash desks until July 1, 2018.
Online cash registers for all types of business! Delivery throughout Russia.
Leave a request and get a consultation within 5 minutes.
What are the penalties for non-use of CCP or violations in its use
Now - about sanctions for non-use of online cash registers (or failure to fulfill obligations to issue buyers with documents that are alternative to cash receipts - BSO and sales receipts). The main of the sanctions under consideration are enshrined in the provisions of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For convenience, they can be displayed in the form of a table.
| Offense | Regulatory norm in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | Sanctions | Notes |
| Sale of goods without the use of cash registers | paragraph 2 of Art. 14.5 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation | 1. A fine for an official of the store (or for an individual entrepreneur, as the owner of the store) in the amount of 25-50% of the proceeds not broken through the cash desk (but not less than 10,000 rubles). 2. A fine for the store as a legal entity in the amount of 75-100% of the proceeds not broken through the cash desk (minimum 30,000 rubles). |
Examples of offenses: 1. Release of goods in the absence of cash registers in the store. 2. Application of KKM, which works incorrectly, with failures. 3. Breaking through a check with an amount less than that transferred by the buyer to the seller. 4. Non-issuance by the service provider of BSO. 4. Non-issuance by a trading company on UTII (IP on PSN) of a sales receipt to the buyer (at his request). |
| Resale of goods without the use of cash registers for an amount exceeding 1,000,000 rubles | paragraph 3 of Art. 14.5 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation | 1. Disqualification for an official - for a period of 1-2 years. 2. Suspension of the store - for up to 90 days. |
|
| The use of CCP that does not meet regulatory requirements | paragraph 4 of Art. 14.5 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation | 1. A warning or a fine for an official (or individual entrepreneur) in the amount of 1500 - 2000 rubles. 2. A warning or a fine for a legal entity in the amount of 5,000 - 10,000 rubles. |
Examples of offenses: 1. Use of old-style cash registers (not online cash registers). 2. Using an online cash register that is not registered with the Federal Tax Service. 3. Using an online cash register that is not included in the register of the Federal Tax Service. |
| The refusal of the store to send the buyer an electronic version of the cash receipt or the seller's failure to issue a paper receipt | paragraph 6 of Art. 14.5 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation | 1. Warning or fine for an official (or individual entrepreneur) in the amount of 2000 rubles. 2. Warning or fine for a legal entity in the amount of 10,000 rubles. |
If the product is sold by an online store, then an electronic receipt is sent to the buyer (by e-mail or in the form of SMS) in any case, without the buyer's request. If the check is not sent, the online store may be fined. A regular store sends an electronic check to the buyer only if he provides the seller with his e-mail or cell phone. A paper check is required. |
The above, and, obviously, rather severe penalties are issued by inspectors of the Federal Tax Service during tax audits - scheduled or unscheduled. Thus, by the time of inspection, the store must be clean for possible suspicions of the above offenses.
But, as practice shows, not all outlets manage to avoid committing these offenses - due to the influence of various factors. Nevertheless, store owners have a chance of being favored by the inspection structures in a number of cases. We will study when this is possible, and on what it depends.
When can fines be avoided?
A store may become a forced violator of the law on the use of cash registers if, for example:
- Will not have time to acquire an online cash register by the deadline.
Related scenarios:
- the existing online cash desk broke down, and they did not have time to order (deliver) a new one;
- the supplier delays prepaid cash desks;
- cash desks were brought, but there is no one to install and configure them (the nearest service center is in another city, half of its specialists are on vacation).
In fact, regardless of the reasons (which, of course, can be much more in comparison with the list above), the store will not be able to use the online cash register, which means it will be considered a violator of the law on the use of cash registers.
However, when considering a situation in which the outlet does not have the opportunity to use the online cash register, in essence, a number of circumstances can be identified that allow us to say that the store should not be fined.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, a state body to which the Federal Tax Service is accountable, in Letter No. 03-01-15/33121 dated May 30, 2017, says, referring to the provisions of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, that only that action of the subject of legal relations that has the sign wrongfulness and testifies to the fault of the subject concerned. If there are irremovable doubts in the assessment of the actions of a person, then such doubts, according to the Office, should be interpreted in favor of this person.
Based on these theses, the Ministry of Finance recommends that inspection bodies, when considering offenses for which, in Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, strict sanctions are prescribed, to study the circumstances indicating that the trading enterprise has taken all the necessary measures to ensure that the conduct of activities complies with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on the application of CCP. And if the store shows that such measures will be taken, the Ministry of Finance recommends that inspectors not fine the outlet or company officials.
One of such measures, according to the Ministry of Finance, may be the conclusion of a contract for the supply of a fiscal drive (the main technological component of online cash registers) in order to modernize the existing CCP. At the same time, the trade enterprise, according to the department, should continue to use old-style cash register equipment - with ECLZ, and issue paper checks to all customers.
Thus, with the highest probability of being protected from fines by the Federal Tax Service, taking into account the indicated position of the Ministry of Finance, businesses that have old-style cash registers and did not have time to upgrade them by the time the mandatory use of online cash registers began.
But when analyzing the provisions of the letter from the Ministry of Finance that we have reviewed, quite obvious legal analogies arise, which would probably allow us to talk about a similar level of protection from fines for any businesses that failed to launch the trading infrastructure based on online cash desks on time (including “from scratch”). ”, during modernization, in the process of replacement, repair, adjustment of CCP).
The main thing for them is to have on hand a document confirming that the store has done everything in its power to equip the cash register infrastructure with cash registers that work and comply with the requirements of the law. If the online checkout is broken, this may be a contract for its repair; if it is delayed along the way, a document confirming the prepayment for its delivery.
In principle, the position of the Ministry of Finance can also be summed up in a situation where a company exempted from the use of CCP is obliged to issue strict reporting forms to customers, but cannot, because they are over, and by the time of settlement they have not arrived from the printing house.
- Will not be able to use the online cash register due to a power outage (Internet).
Everything is more complicated here. In the most general case, you should follow the recommendation: no electricity (in this case, perhaps also the Internet) - no trade. If the sellers nevertheless carry out the release of goods, then the Federal Tax Service will have every right to apply the sanctions we have discussed above to the store.
However, as law enforcement practice shows, in a number of scenarios, owners of trading businesses have the right to expect that inspectors will show loyalty to them and will not fine them. This is possible if, for example:
- Electricity or the Internet was turned off right at the time the store settled with the buyer. In this case, it is legitimate to speak of force majeure circumstances, which, in the general case, relieve the participant of legal relations from liability not only in the context of the implementation of the norms of Law No. 54-FZ, but also, in principle, any other regulatory act.
- It was highly desirable to make settlements with buyers due to the large queue at the cash registers, which had formed by the time the electricity was cut off. And the store decided to break the law by releasing the goods without cash registers.
If there are comments from the inspectors on this matter, the store can argue its actions by saying that stopping trading (especially if people came to a rare rural store in the summer heat for drinks) in such cases can lead to extremely unpleasant social consequences and is unlikely to be limited to simple dissatisfaction buyers.
- Interruptions with electricity and the Internet are observed not only in the store, but throughout the entire area, and even the city. In this case, the refusal of all outlets to sell - at least the most necessary goods (the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not say anything about them, and their vacation without a CCP is also fined) may be simply unreasonable - here even special arguments for the Federal Tax Service may not be needed .
Of course, it is possible that a store that decides to continue trading in such situations may need to prove its case in court. But, if we consider these scenarios in their pure form, then the tax authorities, as a rule, are not inclined to provoke taxpayers into litigation. And if, nevertheless, such a provocation takes place, the store has every chance to defend its case in court.
Thus, law enforcement practice plays an important role in this issue. The fact that at the level of federal legislation severe sanctions are provided for taxpayers, of course, should be taken into account and be a guideline when planning trade. But if a trading enterprise violates the law by force, then it has a chance to avoid such sanctions.
The presence of an operating online cash desk at an enterprise is one of the factors affecting the success of a company passing a tax audit on other grounds. The Federal Tax Service of Russia, in a letter dated July 13, 2017 No. ED-4-2 / 13650 (containing methodological recommendations on tax audits for regional representative offices of the department), indicates that an audit of a CCP of an economic entity can reveal important circumstances in determining violations in business activities. From this we can conclude that ensuring the correct operation of cash registers can play a positive role in the interaction between the store and the Federal Tax Service, even outside the context of the application by inspectors of the sanctions provided for by the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in case of violations of the use of online cash registers by the store.
Summary
Businesses that accept payments from buyers - individuals, from July 1, 2017 must punch checks at online cash desks - unless permanent or temporary exceptions are established for them by law. If an online cash register is not used (documents that replace a cash receipt are not issued), old-style cash registers or those cash registers that are used in violation of the procedure established by law, penalties may be applied to a trading company under the provisions of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If the store does not have an online cash register operating and registered in accordance with the procedure established by law, then by the time the Federal Tax Service checks, its representative will need to acquire documents certifying the fact that the store has done everything in its power to comply with the requirements of the law in terms of equipping cash registers. For example:
- an agreement for the supply of online cash registers (fiscal registrars for their modernization);
- documents confirming the acceptance of online cash registers and those confirming the call of specialists to set them up (for example, receipts for making an advance payment for the services of these specialists);
- documents confirming the BSO order (if the company must issue these forms to customers instead of using CCP).
Provided that trading enterprises follow this approach, it is highly likely that a fine will be avoided.
If the store fails to use online checkouts due to force majeure circumstances or those that predetermine the undesirability of their non-use, then the business owner has the right to rely on the regulatory authorities to show loyalty to him. Or - count on the resolution of the situation in court in their favor.
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for liability in the form of a fine for failure to issue a cash receipt (including in 2017). Consider the regulations that establish the obligation to issue a check and the corresponding liability for its non-issuance.
Obligation to issue a check
The concept of "cash receipt" in the sense given to it by the Government of the Russian Federation, implies a paper accounting document obtained using a cash register and is a confirmation of cash settlement.
The obligation of the seller, upon receipt of cash for the purchase, to issue a cash register check follows from paragraph 1 of Article 5 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the Use of Cash Registers”.
From the Model Rules for the Operation of KKM approved by the Ministry of Finance of Russia (dated August 30, 1993 N 104), it follows that the cashier, having received money for a product (service), must:
- firstly, name the amount received;
- secondly, print a cashier's check on a cash register;
- thirdly, name the amount of change (if necessary) and give it to the buyer with a cash receipt attached.
Failure to issue a cash receipt violates the above obligation.
Check issuance control
Measures to control the fulfillment by business entities of the obligation to issue cashier's checks are carried out by tax authorities (Article 7 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ "On the Application of Cash Registers", Article 7 of the Law "On Tax Authorities" of March 21, 1991 N 943-1).
For this purpose, the tax authorities conduct test purchases.
When buying, the inspector presents the seller with an order from the tax authority to conduct an inspection and a certificate. After the purchase, the inspector draws up the results of the inspection (Letter of the Tax Service dated 03.28.2006 N MM-6-06 /).
The document drawn up based on the results of the purchase is a confirmation of the sale of goods and can be used to prove a violation committed by the seller in terms of non-fulfillment of the obligation to issue a cash receipt (question 15 of the Review of Judicial Practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2 dated June 26, 2015).
Responsibility for non-issuance of a cashier's check
The Code of Administrative Offenses in part 6 of article 14.5 states that the refusal to issue a check to the buyer at his request entails a warning or a fine:
- IP - 2000 rubles;
- officials - 2000 rubles;
- organizations - 10,000 rubles.
Consequently, for the seller in the situation provided for by Part 6 of Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, failure to issue a cashier's check will entail a fine.
In July 2016, a law came into force (Federal Law of July 3, 2016 N 290-FZ), obliging organizations and individual entrepreneurs to use online cash registers. This is a global change in CCP legislation. You can read more about online cash registers in a separate article.
What threatens for an unbroken check in 2018?
With the entry into force of Federal Law No. 54-FZ "On the use of cash registers," organizations and individual entrepreneurs are required to issue receipts to customers, even if they do not ask for them. In this article, we will tell you what the violation of this requirement is fraught with and in what cases you can not break through the document without the risk of being fined.
Why do you need a check?
A receipt notifying of payment for the goods is proof that the purchase was made at a certain time in a particular store. A broken check fixes the amount that has passed through the cash desk of the outlet during the reporting period. If the paper is not issued, the individual entrepreneur and its employees violate the rights of consumers and their own obligations under Federal Law No. 54-FZ. Therefore, the provision of receipts is a mandatory procedure for inspections by the Federal Tax Service.
A cash receipt, bypassing the prevailing practice of some unscrupulous sellers, is not the only opportunity for the buyer to return or exchange the purchased goods. Procedures can be carried out without this document, although its provision is desirable. Therefore, do not deceive yourself and try to circumvent the law in this way. In addition, there are significant fines for not providing checks.
Consequences of violation
Failure to issue a receipt may result in sanctions from the tax authorities. You should be aware that a fine is imposed on any document drawn up according to inappropriate statutory standards and on an unregistered cash register.
- For officials, the amount of recovery is determined from 3,000 to 4,000 rubles.
- Individual entrepreneurs are required to pay a fine in the amount of ¼ or ½ of the amount for which the document was not issued. Moreover, it should not be less than 10,000 rubles. This means that even for 20 rubles that have not been broken through, the company will receive a minimum fine.
- Sanctions from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles are provided for legal organizations.
In some cases, the firm may only receive a warning. It is possible to avoid a fine if the company has not previously been held administratively liable and has not committed violations.
An inspection by the Federal Tax Service may come suddenly in response to a complaint from the company's clients about the non-issuance of a check. The fact of violation will certainly be revealed during the investigation, and not only fines will be applied to the organization, but also regular inspections by the tax authorities.
If the individual entrepreneur did not issue a receipt to the client for payment for the goods due to a malfunction of the cash register or a tape that ended in it, sanctions are also applied to him, since there are no exceptions to the rules for using online cash registers. If the CCP fails, the IP must suspend the cash payment, including the payment started immediately before the breakdown of the device. The same requirements are relevant when the cash tape has ended. However, if it is promptly replaced with a new one, the operator can continue accepting cash.
What check needs to be broken in order not to fall under sanctions?
In accordance with the amendments to the law, cashiers must issue a document confirming payment for the goods to customers, even if the buyer does not require it. The Federal Tax Service explains that a check can be entered in any format - paper, electronic or both at once. The client himself chooses which option is more convenient for him. If the company does not comply with its requirement, the buyer has the right to apply to the Federal Tax Service, and a fine is imposed on the organization.
If the client does not insist on issuing a check, the cashier must punch and give him a paper document. Electronic is knocked out if the buyer indicates his email address before making payment.
When is a check not needed?
The law practically does not provide for cases when individual entrepreneurs and organizations are exempted from issuing a receipt for payment. One of the exceptions is the fact when the buyer makes an advance payment. That is, the goods are not paid in full, and remain with the seller - the purchase and sale transaction has not yet been formalized. As soon as the client pays for the purchase in full, the company is obliged to punch him the document.
In addition, if an organization provides any services to the public and issues strict reporting forms, these documents are equated to checks, and it is not necessary to punch them through the cash desk again.
The amount of the fine for an unbroken check in 2018 for individual entrepreneurs
Law No. 290-FZ of July 3, 2016 introduced a new scale of penalties for an unbroken check when carrying out commercial activities or providing services. For an individual entrepreneur, the amount of the fine increased by 2-5 times. In all the subtleties - when, how and why this fine is levied - our article will help you figure it out.
Application of CCP for IP
Intriguing subtitle, isn't it? Who is an individual entrepreneur is more or less clear - this is an individual entrepreneur. And what is a cash register, the individual entrepreneur knows for sure, and we explain to the rest - this is cash register equipment. And, according to Article 14.15, paragraph 2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, all receipts of funds in the course of entrepreneurial activities must be accompanied by a check on a cash register or any other cash register. And it doesn’t matter at all what you get money for - for a product sold or a service rendered.
Getting money in hand should immediately be accompanied by breaking a check. It is this moment that is very important so as not to be subject to penalties. Quite often, inspection bodies provoke a situation where it is impossible to break a check on time. They leave money on the counter and take the goods themselves while the seller is busy with another buyer. And a lot of other tricks. In any case, the responsibility lies with the seller. Be careful and vigilant. And if the check is not broken intentionally, then you need to be offended only at yourself.
The amount of the fine for individual entrepreneurs if the check is not broken
An individual entrepreneur pays a fine for a check not broken on time, on the basis of the above law of the Russian Federation and amendment 2 to Article 14.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, in the amount of ¼ to ½ of the amount for which the check was not broken, but not less than 10 thousand rubles. This means that if a check for the amount of 200 thousand rubles is not broken, then the fine will be in the amount of 50 to 100 thousand rubles. And if the check is not broken in the amount of 20 rubles, then the fine will be 10 thousand rubles.
Needless to say, individual entrepreneurs are terribly dissatisfied with the innovation and consider these measures “draconian”.
What cash register is needed for the implementation of IP under the simplified tax system
The dissatisfaction of the individual entrepreneur is understandable, but unreasonable. In fact, how else, if not through CCP, you can track the amount of income received. Any concealment of the amount of funds received in the calculation entails a reduction in tax deductions to the state treasury. How can a state exist without taxation? No way. Concealment of income is considered an offense and the offense is at least punishable by a fine.
The cash register for IP must meet the following requirements:
- print a receipt and save information about the operation performed for a long time, regardless of the availability of power supplies;
- the device has a fiscal memory and its drive - a control tape;
- prevent the introduction of deliberately incorrect data and the correction of existing information;
- the device must have a passport, an identification mark and a seal;
- must be registered with the FTS. Moreover, it is possible to register and register a cash register with the Federal Tax Service only if its model is indicated in the State Register;
- be in service in a special technical support service.
An individual entrepreneur can purchase a cash register only from specialized companies that not only sell, but also install and maintain the cash register. A long-term contract is concluded with this technical service center, the inscription "Service" is pasted on the body of the device. Only after all these procedures, you can contact the Federal Tax Service at the place of residence to register a cash register. The tax service enters a secret code that protects the system from hacking, installs a seal on the KKM case and enters a mark on the registration of the device in the passport of the device.
Implementation of settlement operations using BSO
In the absence of a cash register, as well as in cases where the device is under maintenance or due to the lack of a power source, an individual entrepreneur can carry out all cash payments using the BSO. These are strict reporting forms. What is the procedure for working with SBO:
- In this case, all the details of the strict accountability form are filled in, except for the signature, upon receipt of the money, a signature is put, and together with the delivery, the form is given to the buyer. A copy of the check is kept by the IP.
- If the payment is made using a card, then the client's card is taken, a strict reporting form is filled out without a signature, the indicated amount is debited from the card when a confirmation receipt for the withdrawal of the amount is received. A signature is put in the BSO, and then a card with a check filled out in the BSO form is issued to the client.
- The entrepreneur must have either a copy of the form or a spine filled in according to the form, depending on which strict reporting forms are used by the entrepreneur.
- BSOs are filled out strictly according to the form in the order of numbering. Corrections in the form are not allowed, the signature is required if it is provided in the form.
- The damaged form is not thrown away, but crossed out and saved. All forms will have to be reported to the Federal Tax Service.
- At the end of the working day, the entire amount of money received under the BSO is calculated and an incoming cash order is issued for the entire amount that is entered in the cash book. Moreover, only the amount of cash is issued by a cash order.
- Keep copies of the BSO for at least 5 years after the last audit.
The penalty for a strict reporting form that is not issued on time and filled out in accordance with the form is the same as for a check that has not been punched through the cash register. Therefore, it is worth taking their filling and issuance with full responsibility.
That's all that an individual entrepreneur needs to know about the use of cash registers and BSO. There is good news: the fine for individual entrepreneurs for an unbroken check in 2018 will not be increased in size.
What is the penalty for not breaking a KKM check?
Send to mail
Failure to break a KKM check - a fine for this violation is imposed both on the organization and its officials, and on entrepreneurs. It can be revealed during an audit conducted by the tax office, or at the request of an outraged buyer.
Legal provisions for the use of online checks
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 2.1 of the law “On the use of cash registers ...” dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ, enterprises and individual entrepreneurs working with cash registers are required to punch checks when making payments using cash and payment cards. Settlement refers to the receipt and issuance of funds.
Read about what needs to be done if the check was not broken due to a breakdown of the CCP, in the material "Without CCP and without a fine - the Federal Tax Service told when it is possible."
Tax authorities, in accordance with Art. 7 of Law No. 54-FZ, they have the right to monitor the correctness of the use of cash registers and the completeness of accounting for revenue from organizations and individual entrepreneurs. As part of the exercise of their powers, the tax authorities can get full access to the cash register, conduct checks on the correctness of its work, issue orders to impose penalties and eliminate violations. A fine for a check not punched at the checkout can also be imposed in the event of a complaint from buyers to the consumer protection department.
Penalty for non-penetration of a cashier's check and other similar offenses
The fine that threatens the company in case of detection of an unbroken check, in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, can reach up to 10,000 rubles. For an individual entrepreneur or an official, this will cost up to 2,000 rubles. True, if you're lucky, violators can get off with a warning.
However, the absence of KKM checks is not the only violation that entails sanctions. For example, non-use of cash registers threatens the enterprise with a fine in the amount of ¾ to the entire amount of unrecorded revenue, but not less than 30,000 rubles. For a director or individual entrepreneur, other amounts are provided - from a quarter to a half of the proceeds, but not less than 10,000 rubles. (Clause 2, Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Re-identification of the same violation (when hidden revenue reaches 1 million rubles) threatens to disqualify officials for a period of 1 to 2 years, suspend the activities of an enterprise or individual entrepreneur for up to 90 days.
IMPORTANT! According to Art. 2.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, entrepreneurs bear exactly the same administrative responsibility as officials (unless the Code of Administrative Offenses prescribes otherwise). At the same time, Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses does not contain any clauses protecting IP.
Read about other nuances of observing cash discipline in the material « Cash discipline and responsibility for its violation .
Failure to comply with the rules for the use of cash registers, including an unbroken check, is an offense that threatens to impose a fine on both the organization and its officials or individual entrepreneurs. Try not to allow this, and even if a violation has occurred, try to convince the controllers of the unintentionality of your actions and the desire to avoid this in the future.
Be the first to know about important tax changes
Is an individual entrepreneur obliged to issue a check and what is the penalty for violating cash discipline
Each business entity that makes settlements with customers (in cash and through bank terminals) needs to know the regulations established by the Central Bank governing the procedure for conducting cash transactions. The rules of cash discipline for entrepreneurs are simplified in comparison with the rules for legal entities by Instruction of the Central Bank dated 11.03.14 No. 3210-U. What are the features of cash discipline for individual entrepreneurs, what is the penalty for an unbroken check in 2018 for individual entrepreneurs?
Features of cash transactions for individual entrepreneurs accounting documentation

Under the cash transactions of an individual entrepreneur is understood the receipt and issuance of cash from the cash desk.
In this regard, the legislation defines two types of accounting documentation:
- PKO (incoming cash order);
- RKO (expenditure cash order).
Responsibilities for documenting the above documents may be assigned to an accountant (including the chief accountant), an authorized employee, or carried out by the entrepreneur himself. The accountant and the cashier are required to sign the documents. If the IP solely performs both functions, then it is he who affixes the signatures.
An individual entrepreneur must form a procedure for carrying out cash transactions and allow a cashier to work only after reading the specified regulations against signature.

The Decree of the Bank of Russia provides for a simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions for individual entrepreneurs, namely:
- the absence of a cash limit is allowed (the limit value of the cash amount for storage at the cash desk without transferring money to the bank);
- it is not required to form an incoming and outgoing cash order;
- there is no need to maintain a cash book.
Important: the consequences of refusing to draw up credit and debit orders may be abuse of official position and an increase in the number of thefts among employees. Such a decision is justified for entrepreneurs who carry out business on their own, without the involvement of employees.
The fact of receipt of revenue by the entrepreneur can be confirmed by cashier's checks, reports on the closing of the shift, strict reporting forms (BSO). It should be noted that when business entities make settlements with customers using a bank terminal or cash desk, KKM is obliged to issue a cash receipt for any of the operations, and if requested, send the document to e-mail. An individual entrepreneur can issue salaries to personnel with a payroll form No. T-53 or a payroll sheet No. T-49.
Entrepreneurs are allowed to correct errors made in documents affecting the accounting of cash transactions, with the exception of CRS and PKO. To do this, you need to cross out the incorrect information and enter the correct information indicating the date of the adjustment. Corrections must be certified by the signature of the employee who issued the document. You also need to decrypt the fix.

The use of cash registers for individual entrepreneurs in 2018:
- Individual entrepreneurs providing services to the public have a delay in the application of CCP until 07/01/2019, subject to the use of strict reporting forms (SSO) and UTII or PSN. BSOs must be produced by typography or automated systems, such as a computer. No. 54-FZ defines the list of business lines that have the right to operate without a cash register.
- Individual entrepreneurs who are not engaged in the provision of services to the public - entrepreneurs, workers in the retail trade are required to use cash registers. Recently, entrepreneurs have been obliged to use online cash registers, the main difference of which is the presence of direct access to the Internet. A fiscal drive is built into such cash desks, the task of which is to store information about completed transactions and transfer them to the Federal Tax Service. Individual entrepreneurs on UTII and PSN may not apply CCP until 07/01/19. Entrepreneurs in the field of retail trade and public catering can apply their rights if they do not use the labor of hired personnel (the rule also applies to individual entrepreneurs engaged in trade through vending machines). The businesses listed above must issue checks as proof of receipt of cash.
- Individual entrepreneurs engaged in specific activities - there is no need to use CCP when trading from tanks, on the market, when selling non-alcoholic beverages for bottling, as well as selling ice cream, newspapers and magazines, when receiving scrap materials and glass containers from the population.
- Individual entrepreneurs doing business in hard-to-reach (remote) areas may not use cash registers and issue documents to buyers. The subjects of the Russian Federation independently approve the list of remote areas. Cities, district centers, urban-type settlements cannot be classified as such.
The entrepreneur is personally responsible for the introduction of cash registers, controls the total cash turnover, even if there is a cashier in the state.
Entrepreneurs are allowed to make cash settlements under one contract (with a legal entity or individual entrepreneur) in the amount of not more than 100 thousand rubles. All calculations are taken into account. The exceptions are payroll operations, personal needs of individual entrepreneurs, social benefits, as well as the issuance of employees under the report.
Responsibility for violation of cash discipline
Entrepreneurs whose activities are related to cash or non-cash settlements (using a bank terminal) must strictly comply with the established rules, otherwise, such individual entrepreneurs face a fine for violating cash discipline.
A gross violation is the implementation of activities without a cash register.
This is due to the fact that entrepreneurs are required to issue a purchase receipt to the buyer in the following cases:
- the seller sold the goods;
- IP provided a service to a client for which payment was made;
- the customer has previously placed an order and received the service.
 If a check has not been issued for the above operations, the entrepreneur will be checked for the presence of cash registers. For work without a cash register for individual entrepreneurs, a fine is imposed, the amount of which depends on various criteria.
If a check has not been issued for the above operations, the entrepreneur will be checked for the presence of cash registers. For work without a cash register for individual entrepreneurs, a fine is imposed, the amount of which depends on various criteria.
What fine in 2018 will an individual entrepreneur pay for an unbroken check if:
- there is no cash register - ¾ of the total volume of transactions without cash registers, but not less than 10 thousand rubles;
- business does not fall under the law on the use of cash registers or there are malfunctions in cash registers - 5-10 thousand rubles;
- failure to send an electronic check or failure to issue a hard copy at the request of the client - 10 thousand rubles;
- the check is not broken - ¼ or ½ of the price of the goods sold or the service provided, but not less than 10,000 rubles. For example, if a check is not issued for a purchase in the amount of 20 rubles, then you will have to pay 10,000 rubles. upon discovery of a violation.
If the entrepreneur has set a cash storage limit at the cash desk and exceeded it, a fine of 4,000 - 5,000 rubles will be charged.
Control over compliance with the rules of cash discipline is carried out by the IFTS.
During the control measures, the fiscal authorities will check:
- documents confirming the conduct of transactions;
- KKI control tapes, fiscal reporting;
- documents confirming the registration of CCP;
- operational documents of KKM;
- documents containing data on the receipt, accounting and write-off of BSO;
- accounting registers;
- if a cash limit is set - Order;
- expense reports.

Personnel must comply with the rules of cash accounting. However, the IP is responsible.
To conduct a tax audit on compliance with cash discipline, an Order must be issued by the head of the Federal Tax Service. The document indicates the time period during which the verification will be carried out.
Storage of cash
Unlike the material liability of an individual entrepreneur for failure to issue a check, liability for violation of cash storage is not provided.
- Prohibit unauthorized access to the cash register.
- Isolate the cash register, close the doors at the time of the operation.
- Keep money in safes or vaults, the keys to which are provided to a limited number of persons.
- Seal the cash register daily.
- Do not keep money that does not belong to the individual entrepreneur.
- Provide protection during transportation.
The state does not prohibit the conclusion of insurance and collection agreements. The entrepreneur can limit the limit of cash on hand at the end of the working day. Restrictions are set on the volume of receipts or issuance. Having made the calculation, it is required to approve the limit by the Order. After that, the entire amount of the over-limit amount must be handed over to the bank for further crediting to the current account.
The legislation defines an exhaustive list of the intended use of cash from the cash desk:
- personal expenses of an entrepreneur - the law allows entrepreneurs to withdraw any amount from the cash desk, without any restrictions, if the purpose of their use is for purposes not related to entrepreneurial activity. It is important to avoid arrears in tax and insurance payments;
- payment for services, goods or works;
- staff salaries;
- social payments (material assistance, allowance);
- insurance indemnities under insurance contracts to persons who have previously paid the insurance premium in cash;
- settlements with accountable persons - funds are issued for business, travel and representation expenses. Extradition is carried out only on the basis of the application of the employee. Within 3 days from the end of the period for which the funds were issued, an advance report must be submitted, with documents confirming the expenses attached. Otherwise, it is impossible to add the spent amount to expenses;
- when returning goods previously paid for in cash, the IP must also refund in cash (as well as for outstanding work or services that were not provided).
Documents confirming the fact of receipt and expenditure of cash must be kept for 5 years. It is not recommended to reduce such a period.
Thus, the entrepreneur is obliged to develop and carry out activities aimed at the safety, storage, transportation of cash. It is also necessary to establish regulations and terms for checking the actual amount of cash. Cash transactions can be carried out in a general manner (with the obligatory formation of cash documents, maintaining a cash book and observing the established cash limit) or simplified (without the formation of the documents listed above). Failure to comply with the rules of cash discipline established by law will lead to bringing the entrepreneur to administrative responsibility.
Order of the Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation of January 13, 2008 N 5 "On the burial of the dead (deceased) military personnel, citizens called up for military training, and persons dismissed from military service" (as amended and supplemented) Order of the Minister of Defense of the Russian […]
The concept of cash discipline combines a number of norms and restrictions related to the receipt, issuance, storage of cash at the enterprise, in case of non-cash payments - their accounting as part of cash transactions. Any manipulations with cash, including the issuance of salaries, the acceptance of payments for goods and services, as well as their timely documentation, are called cash transactions. The set of norms adopted as the basis for maintaining a cash desk is not established by the management of private companies, but is determined by legislative acts of the Russian Federation.
Penalty for an unbroken check for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs in 2018
A new scale of penalties for an unbroken check for services rendered or for commercial activities was introduced by Law No. 290-FZ in July 2016. For violators - individual entrepreneurs, the amount of fines increased by 2-5 times. In accordance with article 14.5, clause 2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, any operation of receiving funds by an entrepreneur is accompanied by a check on the cash register, and the proceeds are taken into account both for the goods sold and for the service provided.
The IP penalty for failure to issue a cash receipt in 2018 is provided for by the above law and amendment 2 to Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses and amounts to an amount of ¼ to ½ of the cost of the service provided or goods sold, but not less than 10,000 rubles. In practice, it looks like this: if a check is not issued for the amount of 200,000 rubles, then the fine will be from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles, but if the purchase amount is only 20 rubles, then the fine for a check not punched at the checkout will be 10,000 rubles.
Penalty for the lack of a cash register for individual entrepreneurs and LLC

Any organization or individual entrepreneur making cash settlements with customers in cash or bank cards is obliged to hand over to customers a check from a registered cash register. Work without a cash register is simply prohibited. A mandatory check document is issued in cases where:
the seller sold the goods;
employees of the company provided paid services to the client;
the client received the previously ordered service.
If a check for the above services is not issued, a fine will be imposed on the work of an organization or individual entrepreneur.
When exercising control and supervision over compliance by entrepreneurs with the law on CCPs, the tax authorities monitor settlements using online cash registers, evaluate the completeness of the data provided by organizations and record the revenue received by them. Violators will be fined for not using the IP cash register, in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Type of administrative violation | Type of punishment for an official | Type of punishment for legal persons and IP |
|
Non-use of cash registers in cases established by Russian law | Fine from ¼ to ½ of the amount of the calculation carried out without the use of cash registers, but not less than 10,000 rubles; | A fine from ¾ fourths to the full amount of the calculation carried out without the use of LTT, but not less than 10,000 rubles. |
|
The use of LTT that does not meet the requirements of the new edition of Art. 4 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ. | Fine from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles; | Fine from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles |
|
Violations in the work of CCP in accordance with the requirements of Art. 4.2. "Procedure for registration, re-registration and de-registration of cash registers" of Federal Law No. 290-FZ in | Fine from 1500 to 3000 rubles | Fine from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. |
|
Non-direction by an organization or an individual entrepreneur when using a cash register to a buyer of a cash receipt in electronic form. | Fine 2,000 rubles; | A fine of 10,000 rubles. |
|
Non-transfer by an organization or an individual entrepreneur, when using a cash register receipt, to the buyer at his request in cases provided for by law | Fine 2,000 rubles; | Fine 10,000 rubles |
All new fines for non-use of cash registers in 2016 came into force on July 15, 2016, and the fine for non-use of cash registers for individual entrepreneurs in 2018, the so-called online cash registers, are effective from February 1, 2017.
Penalty for exceeding the cash limit in 2018

The concept of "cash limit" means the maximum allowable amount of cash in the cash vault, safe or cash desk of the organization by the end of the working day. A similar norm was introduced by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, however, the accounting department of the enterprise sets its maximum individually at the beginning of each calendar year.
Cash surpluses may legitimately be allowed on certain days. Valid reasons, according to paragraph 2 of the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U, are:
payment of wages and various types of assistance, but not more than five working days after the withdrawal of funds from the company's settlement accounts;
carrying out cash transactions involving cash on non-working days or holidays.
Other circumstances cannot serve as a justification for exceeding the limit and entail penalties.
The law allows selected categories of small business commercial companies, enterprises, organizations, individual entrepreneurs to cancel the cash limit. To abandon the limit amount, you do not need to take any special actions, it is enough to simply comply with certain standards Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 “On the Procedure for Conducting Cash Transactions by Legal Entities and the Simplified Procedure for Conducting Cash Transactions by Individual Entrepreneurs and Small Businesses »:
limited number of staff - does not exceed 100 people for the past calendar year;
marginal income for services performed and goods sold - no more than 800,000 rubles, excluding VAT;
participation in the authorized capital of other legal entities - no more than a quarter of the share.

If any of the organizations falls within the scope of these requirements, it can keep any amount of funds in cash.
What administrative penalty is imposed in cases of violation of the cash limit? Legal entities are punished in the form of a fine in the amount of 40,000 to 50,000 rubles, individual entrepreneurs and officials (accountant and manager) are subject to penalties in the amount of 4,000 to 5,000 rubles.