Penalty for not having a receipt. Mild punishment for an unbroken check. What gives CC
If the tax authorities have fined your company for an unbroken cash receipt, you can appeal against the decision on the fine to the arbitration court. What arguments will allow you to significantly reduce the fine or avoid liability altogether, says our expert Elizaveta MAKAROVA.
Who is guilty
According to the Code of Administrative Offenses, both a company and a specific employee can be fined for an undrawn cashier's check. But so far, arbitration judges have not formed a unanimous opinion about when an enterprise should be responsible for the mistakes of its employee, and when not.The Supreme Arbitration Court considers that the firm is responsible for its sellers as they trade on its behalf. That is, if the employee did not knock out the check, then not only him, but also the company can be fined (Decree of December 9, 2003 No. 10964/03). The Constitutional Court holds the same opinion (ruling of December 14, 2000 No. 244-O).
But there is a very important point: no one can be held administratively liable if his guilt is not established (Article 1.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses). The firm will be to blame only if it did not ensure that the rules for the use of the cash register by a particular employee were followed.
You are not required to prove the firm's innocence. It is the tax authorities who will have to prove that you did not take all the measures in your power to prevent the violation. So let them think that it was you who did not. And all fatal doubts the court will interpret in your favor.
We translate the arrows to the employee
Since the penalty for an unbroken check is at least 10 times greater for the firm than for the seller, one should try to transfer all responsibility to him. To do this, in the employment contract with each seller in the section "Obligations" write the following:"one. When selling goods for cash or using plastic cards, the employee is obliged to punch cash receipts and issue them to customers at the time of receipt of money. Otherwise, the cashier-operator is liable in accordance with the current legislation.
Write down the seller's obligation to use KKM in his job description, approved by order of the general director. Also print out the Model Rules for the Operation of KKM, approved by the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 30, 1993 No. 104, and familiarize the employee with them against receipt.
An employment contract, a job description and a receipt from the cashier on familiarization with the rules for operating KKM can be drawn up retroactively and presented after verification in court. If the tax authorities try to object that you did not show them these documents during the audit, the arbitrators most likely will not listen to them - you were not obliged to do this (an example of this is the decision of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District of October 22, 2003 No. A31-2241 /16).
When drawing up a protocol on an administrative offense, the inspector will require an explanatory note from both the director of the company (or his deputy) and the seller. The head of the company must write in it that the administrative violation occurred solely through the fault of the employee, who grossly violated both the job description and the terms of the employment contract.
The employee must take the blame. That is, indicate in the explanatory note that the violation occurred through his fault, since he was familiarized with his obligation to apply the CMC in advance.
If you complete all the documents listed above, the court will most likely support you and cancel the fine from the company and the director.
We are not responsible for others
Unfortunately, not all judges believe that the condition of the employment contract on the obligation of the seller to use CCM exempts the company from administrative punishment.For example, the Federal Arbitration Court of the Moscow District indicated that even if the employee’s employment contract provides for his responsibility for not using cash registers, this will not save the company from a fine (decree dated December 11, 2003 No. KA-A40 / 9801-03).
But in any case, the company should be responsible only for the actions of its employees. One company managed to avoid a fine because the person who violated the sale rules was not an employee. At the trial, representatives of the company presented extracts from the staff list and a register of information on the income of individuals. In these documents, the seller who violated the law was not listed. The Federal Arbitration Court of the North-Western District released the company from the fine (decree dated September 1, 2003 No. A56-34686 / 02).
Another firm found such a way out. She entered into a service agreement with an entrepreneur. Under this agreement, the company transferred its goods to him, and he had to make settlements with buyers.
Although the goods did not belong to the entrepreneur, he was responsible for the use of cash registers. The name of the company did not appear on the checks either. However, the tax inspectorate punished not an entrepreneur, but a company for not using CCP. The arbitration court canceled the fine. The judges noted that since the company itself did not make settlements with the population, it was impossible to hold it accountable for not using cash registers (Decree of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated November 11, 2003 No. A72-4338 / 03-E352).
Than to pay a fine, it is better to give
Any firm is required to issue a check if it sells a product, work or service for cash. But if you want to give someone something as a gift, you don’t need to punch a check. That is why some companies do this. In the store, they put up an announcement with something like this: “If you were not given a check, your purchase is at the expense of the institution.” If the cashier does not accidentally break the check, the buyer will simply be returned the money. It turns out that the goods were presented, which means that there is nothing to carry through the checkout.Such a measure insures against control purchases and will serve as an additional argument that the company is not to blame for not using CCP. On the contrary, she did everything to avoid it.
In the “Obligations” section of the employment contract with the seller, you need to discuss: if you didn’t break the check, consider that you gave the goods to the buyer. It might look like this:
"2. The employee is obliged to return the money for the goods to the buyer if he did not break the check for the purchase or broke the check for a smaller amount. In this case, the goods are considered transferred to the buyer free of charge.
3. The employee bears full financial responsibility for the goods transferred to the buyer free of charge.
It's better than paying tens of thousands of rubles in fines. And employees will treat their duties more responsibly.
Pay attention to this moment. Tax authorities check the use of cash registers, but this is not tax control. Therefore, the norms of Law No. 134-FZ of August 8, 2001 “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs during state control (supervision)” fully apply to inspectors. Article 7 of this law establishes the procedure for appointing an inspection.So, one "crust" of the taxman when checking cash registers is not enough. The inspector must have an instruction from the head of the inspection specifically to conduct an inspection of the application of the CCP. Any other clause (for example, “it is instructed to check the procedure for compliance with cash circulation, conducting cash transactions”, etc.) does not give the right to check the correct use of the cash register. These are completely different articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses.
The order for the audit must indicate the timing of its conduct, the name of your company, position and full name. inspector. If the protocol and the act of verification do not indicate what measures the company has not taken to apply the cash register, you can safely appeal the decision to hold the company liable in court. The main thing is not to miss the deadline set for this - ten days from the date of receipt of a copy of the contested decision.
Penalty for an unbroken cashier's check:- from the company - from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles;
- from the head of the company (entrepreneur) - from 3000 to 4000 rubles;
- from the seller - from 1500 to 2000 rubles
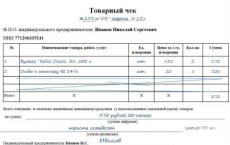
A cash receipt is well known to every modern person. This document is issued by cashiers in supermarkets and shops, as well as other organizations involved in the sale of goods. Many entrepreneurs who decide to open an individual entrepreneur are wondering about the need to install cash equipment at the very last moment. And absolutely in vain.
Cash equipment must be used every time a customer pays in cash. At the same time, non-issuance, as well as non-breaking of cashier's checks, is a very common violation that is detected during inspections by tax services.
What is a cashier's check for?
The cash receipt, first of all, is a confirmation of the completed transaction. When this document is broken, the amount of money transferred through the cash desk for the reporting period is fixed. If the transaction is made "by the cash register", then this is a direct violation of the client's rights, and also runs counter to the concept of cash discipline.
The check contains information such as:
- IP name;
- TIN of the IP organization;
- transaction amount;
- date and time;
- check number, CCP and ECLZ;
- serial number of the PDA;
In some cases, the name and quantity of the purchased goods are printed on the cash receipt.
Contrary to popular belief among unscrupulous sellers, an unbroken cash receipt or the issuance of its alternative (sales receipt) does not deprive the client of the opportunity to return the money for the purchased goods. And therefore, such a “cunning” can only result in additional problems, a fine and unwanted attention from the tax service. 
It should be noted that the inspection bodies are very attentive to the issue of issuing cash receipts. If there is suspicion, they take the entrepreneur, as they say, “on a pencil” and show more zeal during inspections, which greatly increases the chances of getting a fine for some minor deviation from strict rules.
Failure to issue checks and consequences
The current legislation provides for liability in the form of a fine for an unbroken and unissued cashier's check. It should be noted that this rule also includes any other documents issued using cash registers that have not been registered or do not meet the requirements.
In case of detection of the fact of non-issuance of a cash receipt, an official is fined in the amount of three to four thousand rubles. Legal entities in a similar situation will have to fork out ten times more.
In some cases, a fine can be replaced by a warning, but only if two conditions are met:
- Up to this point, the individual entrepreneur has not committed administrative offenses;
- During the inspection by the tax inspectorate, no other violations were revealed.

In other words, an individual entrepreneur can only avoid the penalty for not issuing a check once during the entire period of work.
Non-issuance of a cash receipt is detected only during the inspection of individual entrepreneurs or legal entities by tax officials. True, it should be noted right away that complaints from buyers can serve as a reason for the inspection of the IP. Repeated violations of cash discipline sooner or later cause close attention from the relevant government agencies, which ultimately turns into big trouble. And if the amount of the fine may seem completely insignificant to many entrepreneurs, then the alternative in the form of excessive attention from the inspection authorities will cause much more trouble and headaches.
When the CCT is faulty
Any technique has an unpleasant property to break down and fail. And cash registers are no exception. Failure to issue a check can be due to both technical reasons and the fact that the device simply ran out of tape. In any case, the position of the law remains unequivocal: a check is obligatory and must be issued, no check - no sale. Otherwise, a technical malfunction is equated to a deliberate violation of laws and is punishable by a fine.
According to the rules, in the event of a KKM malfunction, the seller must stop accepting cash and cancel the transaction if it had already been started at the time of the malfunction. If the machine simply ran out of tape, then it is permissible to replace it and continue its work. Otherwise, the entrepreneur may be fined.
Forgery of checks
There are many reasons for counterfeit cash receipts. Some companies and individual entrepreneurs commit such an offense in order to reduce taxes, buyers do this in order, for example, to get past security in a supermarket, presenting a document made in advance. In any case, a fake is recognized sooner or later and entails undesirable problems described in Federal Law N54.

It should be noted that the forgery of checks is also complicated by the fact that on each document the PDA code is printed, which is generated by the ECLZ from such data as the amount, date, time and check number. Even with a very strong desire to decipher such a combination of symbols on your own, it is almost impossible, and generating it manually is even more so.
Moreover, in each building of the tax inspectorate there is a special box where everyone can place a cash receipt for verification. Employees of this institution periodically check the contents of the box for compliance with the PDA code. Moreover, the authenticity of cash receipts can be checked independently. To do this, it is not at all necessary to leave your home, you just need to fill out a special form on the official website of the tax office. If a forgery is detected, the organization that issued the fake document is threatened with an unscheduled check.
When can you do without a check?
According to the current legislation and Federal Law No. 54 of May 22, 2003, in particular, an individual entrepreneur has the right to refuse to use cash equipment in a number of cases:
- If the activity of the individual entrepreneur is related to the provision of services to the population. In this case, strict reporting forms are issued, which act as an alternative to cashier's checks;
- Use of certain taxation schemes. An individual entrepreneur may not issue a cash receipt on completely legal grounds if PSN or UTII are used. This exception includes the types of activities provided for by paragraph two of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of Russia. However, the issuance of an alternative in the form of a sales receipt, receipt or any other document confirming the receipt of cash is required.
In other cases, non-use of the cash register is illegal.
It should be noted that a cash receipt cannot be replaced by another document, with the rare exceptions noted above. If, instead of a cash register, the client receives a sales receipt, invoice or any other paper, he will have the right to send a complaint to the appropriate authorities.
They did not issue a cash receipt - the situation is quite common and needlessly ignored by most buyers. Failure to issue a cash receipt can complicate the process of returning the desired purchase, if suddenly the product turned out to be defective or of inadequate quality. What to do in such a situation, what sanctions threaten the seller, whether sellers should always issue a cashier's check, and when non-issuance of a check can be done legally, you will learn from this article.
Issuing a cash receipt is the responsibility of the seller or organization. After all, this small piece of paper is irrefutable evidence of the conclusion of a transaction between the consumer and the seller for the sale (acquisition) of a certain type of product. What to do in a situation where the seller did not issue a cash receipt? Claim it right on the spot! After all, the presence of this receipt will provide a guarantee that the buyer will be able to return the defective product during its warranty period. If the seller deliberately tries to persuade the buyer by force of persuasion to purchase goods without a cash receipt, then this should lead the buyer to the idea of whether it is worth doing business with such a negligent merchant.
In situations where a purchase is necessary and there is simply no other alternative, you should not despair either. The presence of witnesses to the purchase in the event of a possible exchange will benefit the buyer. In addition, the process of purchasing goods can be recorded on a video of a mobile phone, indicating the date, time and place of purchase. This is due to the provisions of the Consumer Rights Protection Law.
Seller's obligations and penalties
Sellers, on the basis of Article 5 of the Federal Law - No. 54 of May 22, 2003, when the client pays for the purchase of goods in cash, are required to issue a cash receipt. The standard rules for the operation of cash registers state that the seller, upon receipt of funds for the purchase of goods or services, must:
- State the total amount of money received from the buyer.
- Print a cash receipt indicating the name of the product or service, the date and time of its sale, the cost of the product or service. The receipt must also contain information about the name of the organization selling the goods or services, its details, other data among which the method of payment (cash or non-cash) may be indicated.
- Announce the amount of change, at the request of the purchaser.
Violation of one of these points means a violation of the sale procedure. This means that the seller can be held administratively liable in the form of a fine, the amount of which varies from 3,000 to 4,000 rubles for individuals; for legal entities, the amount of the fine is quite significant and ten times more than the amount for individuals. This is due to Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses.
There are situations where the seller may legally not issue a cashier's receipt and therefore it is imperative for potential consumers to familiarize themselves with this information. Based on Federal Law No. 54, sellers may not use a cash receipt if they offer the public to purchase a certain type of service, and instead of a cash receipt, they use strict reporting forms.
Or in cases of application of UTII and PSN, which is not a contradiction to Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But at the same time, the legal requirement, voiced by the client about the desire to receive a cash receipt, cannot be violated.
Did the sellers give you a cash receipt? Do not despair - you can file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor, the Tax Service of the Russian Federation or the Society for the Protection of Consumer Rights. These organizations have effective and efficient ways to influence negligent sellers. The most insignificant of them are test purchases, according to which the verdict of the organization is issued and, possibly, the procedure for imposing penalties is carried out. If you were not given a check, then be sure to make an entry in the book of complaints and suggestions, let other potential clients of this organization know about the dubious inclinations of a negligent seller to save on taxation and conduct business contrary to the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Remember - a cashier's check is required to be issued, only with the exception of a few of the above provisions! In difficult situations, when you were not given the coveted cash receipt, and then there were difficulties with the return of the goods, it is most reasonable to seek legal assistance from the Legal Expert company. Our specialists will be able to advise their clients in detail and tell about possible actions in this situation in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. In the most critical situations, we are ready to assist in full legal support and bringing the case to court.
In contact with
When conducting cash settlements, as well as settlements using payment cards, all organizations and individual entrepreneurs must use cash register equipment included in the CCP register, except for the cases established by the Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ (clause 1 article 1.2 of the Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ).
Organizations and entrepreneurs when making cash payments at the time of payment for goods (works, services) are obliged to issue (send) to buyers (clients) cash receipts or strict reporting forms (clause 2 of article 5 of the Law of 05.22.2003 N 54-FZ). For non-compliance with this requirement, the company (IP) faces a fine for selling without a cash receipt.
Penalty for not issuing a cash receipt 2019
Control over the fulfillment by organizations and entrepreneurs of the obligation to issue cash receipts is carried out by tax authorities (Article 7 of the Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ).
For non-issuance (non-direction) by an organization (IP) when applying a cash register receipt to a buyer (client) of a cash receipt or a strict reporting form, the norms of the current legislation provide for a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine. The penalty for not issuing a cashier's check will be (Clause 6, Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for an individual entrepreneur or an official in the amount of 2,000 rubles;
- for a legal entity in the amount of 10,000 rubles.
Penalties for an unbroken cash receipt 2019
The sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services) by an organization (entrepreneur) without the use of cash registers in cases established by law shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine. The penalty for an unbroken cashier's check will be (Clause 2, Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for an individual entrepreneur or an official in the amount of ¼ to ½ of the amount of an unbroken check, but not less than ten thousand rubles;
- for a legal entity in the amount of ¾ to the full amount of an unbroken check, but not less than thirty thousand rubles.
Is it possible to avoid liability for non-issuance of a cash receipt 2019?
Organizations and entrepreneurs can avoid liability for the above offenses, but only if the following conditions are simultaneously met (note article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- violations have been corrected;
- the tax inspectorate did not have information about violations;
- the IFTS sent an application and documents confirming the violation, which are sufficient for the tax authority to establish the event of an administrative offense.
Read about how to correct errors when issuing cash register checks (including if a check is not issued on time).
For an unbroken check or a check not issued to the buyer, LLC may incur administrative liability. The minimum penalty is a warning, and the amount of the fine starts from 5,000 rubles. In case of repeated violation, the activities of the perpetrator may be suspended for up to 90 days.
Citizens make purchases in the store, on the Internet, pay in cafes. The seller is obliged to issue a document confirming the payment made. If this rule is violated, then a fine for an unbroken check for an LLC is imposed as a punishment.
Table 1. Responsibility for not issuing a check to a customer under federal law
| Regulatory document | Summary | Size of punishment |
| Part 2 Art. 14.5 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation | Do not use cash registers, if its use is necessary | From ¾ to the whole amount of the calculation, but not less than 30,000 rubles. |
| Part 3 Art. 14.5 Administrative Code | Repeated non-use of cash registers, when the amount of settlements in two cases amounted to 1 million rubles. and higher | Administrative suspension of activities up to 3 months |
| Ch. 4 Art. 14.5 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation | Use of a CCP that does not meet certain requirements | From a warning to a fine in the amount of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. |
| Ch. 6 Art. 14.5 Administrative Code | Non-direction in electronic form or non-transfer of a printed check to the buyer at his request | Warning or a fine of 10,000 rubles. |
If a person independently, voluntarily and in writing declares to the tax authority about a committed offense that falls under the above sanctions, he may be exempted from administrative liability.
Will liability increase in 2019?
Failure to issue a cash receipt to the buyer in 2019 will not entail a tightening of the punishment existing under Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
It is interesting! Large-scale changes to Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation were made in 2016. Up to this point, it consisted of only two parts. A limited liability company could be fined for the second of them in the amount of 30,000 to 40,000 rubles. There was no concept of repeated violation, suspension of activities was not envisaged as a punishment.
When can an LLC be fined?
The seller is obliged to punch and issue a check to the buyer when selling goods, performing works and services. In this case, the consumer can pay:
- In cash;
- through electronic payments;
- by using .
The latter option is possible through a bank terminal (acquiring) specially installed at the seller. If this rule is ignored, the violator will be held administratively liable.
An innovation of recent years is the use of online cash registers when calculating. Data from this device is transmitted in real time to the tax authorities. If the check to the buyer was knocked out incorrectly, he has the right to complain about the company. The appeal is also carried out online.
The advantage of such a device is the ability to accept payments even at night and on holidays, while sending electronic receipts to customers (example: online stores).
Attention! The Internet is required for the operation of the online cash register. In the absence of a connection, unsent data is stored in the device itself and, when a connection appears, it is transferred to the Federal Tax Service.
About the consequences of non-use of cash registers under the new rules, the reasons for the introduction and the principles of operation of online cash desks in the following video:
What is a check for?
The document fixes the amount that has passed through the cash desk of the enterprise. A report is prepared at the end of the working day. And if unreceived revenue is found at the cash desk (the money was accepted, the check was not knocked out), this indicates a violation of the seller’s work and may lead to punishment during an audit by the tax authorities.

Who may not apply CCP
Organizations may not officially use the cash register:
- when selling printed materials (newspapers and magazines);
- providing meals to students and employees of educational institutions during the educational process;
- selling securities;
- carrying out peddling trade in goods;
- repairing shoes, making keys;
- accepting glass containers from citizens;
- stalls selling ice cream, milk, soft drinks, water;
- performing religious rites;
- library system.
A complete list of subjects exempted from the use of CCPs is determined by Article 2 of the Federal Law No. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003 "On CCP".
When there is no liability
If the buyer makes an advance payment for a product, work or service, then the seller may not knock out a check for him. This document is subject to registration only after full payment.
When an enterprise provides services to citizens and issues strict reporting forms for accepted payment, there is no need to additionally beat out checks.
How to dispute a fine
A protocol on an administrative offense under Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is authorized to be drawn up by an employee of the tax authorities. Then a decision is made to impose a sanction. It is sent to the person held liable by registered mail or issued against signature.
You can try to cancel the imposed fine by appealing it to the arbitration court. In this case, it is important to remember the deadlines: the claim must be prepared and submitted within ten days from the date of receipt of a copy of the decision to apply the sanction.
Can sanctions be reduced?
Parts 4 and 6 of Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provide for a warning as the minimum punishment. Therefore, when considering an administrative case, a representative of an LLC must remember this, and if the fact of a violation is obvious, insist on the application of this particular form of responsibility.
Another way to try to avoid punishment is to refer to Article 2.9 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation when appealing. It provides for the possibility of exemption from liability in case of insignificance of the committed misconduct.
What happens if you don't pay the fine
An LLC that has been fined must pay the amount specified in the decision within 20 days from the date it comes into force at the request of the tax authority. If this is not done, then the following consequences will occur:
- within two months, the tax authority will decide on the collection of a fine at the expense of the funds of the LLC;
- if the tax authority misses the above period, then it has the right to apply for the recovery of a sanction to the court.
The last action is possible within six months from the date of expiry of the term for payment of the fine on demand.
In case of insufficient funds to pay off the sanction, the tax authority may issue a resolution on the recovery at the expense of the property of the LLC and send it for enforcement to the bailiffs.
Payment Methods
It is possible to pay a fine:
- according to the details specified in the resolution, from the settlement account of the LLC;
- by bank card - through terminals, online banking.
Information about the repayment of the fine enters a special system of state and municipal payments.
Normative base
The regulatory framework for the enforcement of a fine for a check not issued to the buyer is as follows:
- article 32.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation "Execution of a decision on the imposition of an administrative fine";
- article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - collection of a fine at the expense of the guilty person's funds;
- article 47 of the Tax Code “Collection of tax, fee, insurance premiums, as well as penalties and fines at the expense of other property of a taxpayer (tax agent, payer of a fee, payer of insurance premiums) - an organization, an individual entrepreneur”.
Higher education. Orenburg State University (specialization: economics and management at heavy engineering enterprises).
October 19, 2018 .